What is Regulatory Compliance?
Regulatory compliance is the process of complying with applicable laws, regulations, policies and procedures, standards, and the other rules issued by governments and regulatory bodies like FINRA, SEC, FDA, NERC, Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), etc.
Depending on the industry and jurisdiction, regulations vary significantly. Large organizations with a global footprint need to comply with pertinent laws and regulations in all the countries they operate in, and from. Some industries, such as financial services, information technology (IT), and healthcare, face numerous and often complex regulations and compliance frameworks due to their impact on the economy, business, and health infrastructure respectively. Additionally, many of these industries are also at significant risk of cyber breaches, due to the increasingly complex and evolving cyberattack surface.
As a business grows and expands, the regulations it is subjected to also increase in scale and volume, often becoming complex due to overlapping jurisdictions of multiple authorities. This requires an organization to implement the right measures, policies, and processes to ensure compliance.
This page provides a comprehensive overview of regulatory compliance and its importance, the benefits of regulatory compliance, the consequences of non-compliance, and the best practices to follow to achieve regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Compliance Examples
Some of the major regulatory compliance examples related to financial and non-financial sectors include the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), and the European Union’s (E.U.) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory requirements are legally binding rules established by government authorities or delegated bodies to control an industry, process, or sector. Organizations must adhere to these requirements to avoid penalties and ensure responsible conduct.
Regulatory Compliance in the US
In the US, several laws and regulations are in place to protect various stakeholders, including the business itself.
Compliance laws protect consumers from any harmful consequences of the firm’s operations, help the firm protect its reputation, and help senior management and leadership avoid criminal liability. These laws, regulations, and guidelines are industry-specific and some of them have dedicated oversight bodies that ensure implementation.
For example, the financial industry is governed by legislation including the Dodd-Frank Act and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX). The Dodd-Frank Act was brought into effect in 2010 to facilitate financial stability by augmenting transparency and accountability. Regulatory compliance of banks concerning speculative trading, investment activities, and reserve requirements was tightened as a direct consequence of this Act. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) was created to protect stakeholders of publicly traded companies from fraudulent accounting and financial practices. SOX regulates the activities of corporations, such as the certification of financial reports and corporate record-keeping.
Further, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was created to safeguard the data and interests of people covered through health insurance and governs the storage and privacy of their personal medical information and data. Legislations such as HIPAA further serve as a starting point for instituting a comprehensive cybersecurity program in place.
Major regulatory agencies in the US include:
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) An independent agency that enforces antitrust laws which are non-criminal for establishing a competitive market and protecting consumers from deceitful business practices.
- The Occupational Health & Safety Administration (OSHA) This body regulates working conditions by preparing and enforcing standards to provide a safe and healthy workplace.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) The FDA regulates companies that are involved in manufacturing food products, cosmetic products, and drugs. Its regulatory powers also extend to the manufacturers of medical devices.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) It is a non-regulatory agency that develops standards and guidelines to help meet specific regulatory compliance requirements such as IT and data security.
Regulatory Compliance in the EU and Other Major Geographies
The European Union is a supranational entity and therefore its regulations apply to all its member countries. It established the European Systemic Risk Board (ESRB) for financial supervision and has independent entities such as the European Banking Authority (EBA) and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) which set up technical standards.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) includes regulations that apply to organizations collecting data from EU citizens irrespective of the location of the organization. Further, GDPR applies to the data storage of residents within the EU even if they are not EU citizens.
Countries outside the EU in Europe such as the United Kingdom have their own regulatory compliance frameworks and authorities such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) to preserve market integrity.
While mandates of regulatory compliance differ from country to country, similar laws to SOX exist in various countries such as the Corporate Law Economic Reform Program Act 2004 (CLERP 9) of Australia and Deutscher Corporate Governance Kodex (DCGK) of Germany.
In Canada, unlike the majority of countries, there is no federal regulatory agency for securities. Agencies within the provinces and other territories collaborate to regulate trading in securities.
Why is Regulatory Compliance Important?
Regulatory compliance is important to uphold the integrity of business processes, protecting public interest as well as stakeholder interest. It ensures that businesses operate fairly and ethically. When businesses are open and transparent about their regulatory compliance mechanisms, trust and goodwill among clients and business partners increase. This can, over time, improve brand perception and increase the overall profitability of the organization.
With good regulation, consumers are protected from harmful and fraudulent actions taken by business entities such as predatory mortgage lending, which led to the subprime mortgage crisis of 2008. At the same time, directors and managers of businesses that follow regulatory compliance can steer clear of criminal liability and premature career termination due to actions that they may be held directly responsible for.
Additionally, formulating a solid regulatory compliance strategy helps organizations stay on top of risks by being future-ready.
What are the Benefits of Ensuring Regulatory Compliance?
Organizations that maintain consistent regulatory compliance management can reap significant benefits and outcomes both in the short term and over an extended period of time. Important benefits include
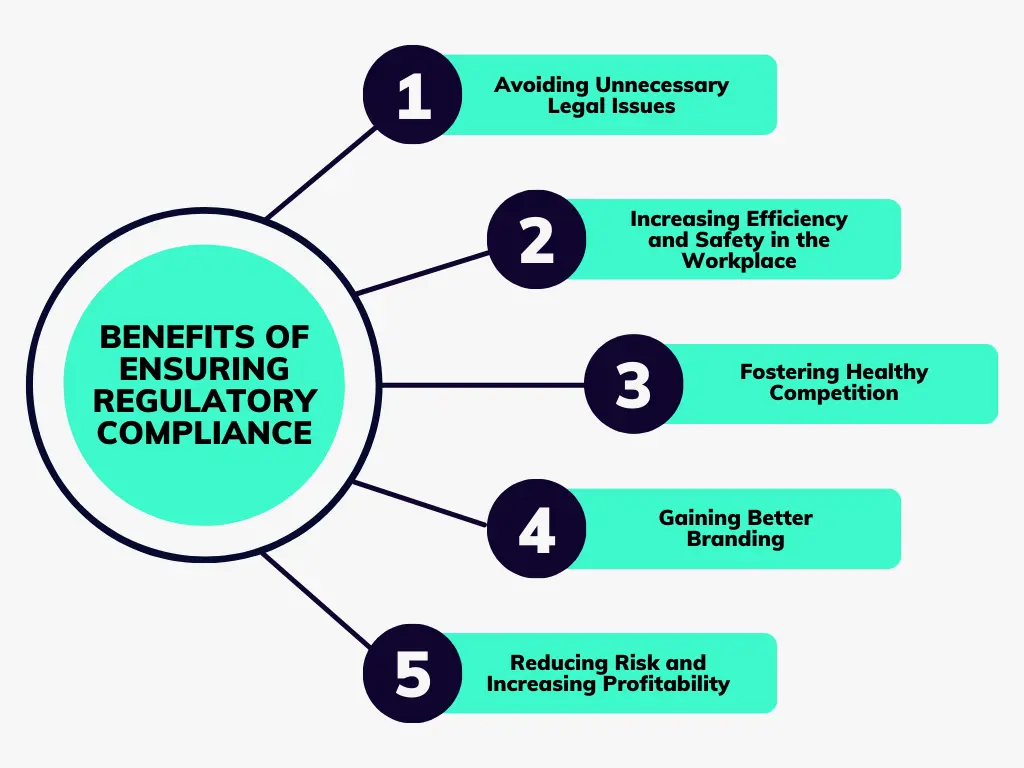
Avoiding Unnecessary Legal Issues
Regulatory compliance frameworks ensure that all necessary legal obligations are met. For example, industries that require the collection and storage of large amounts of user data can avoid legal issues by following regulations such as GDPR. The cost of compliance, as a result, is much lower than non-compliance.
Increasing Efficiency and Safety in the Workplace
Implementation of rules against discrimination and harassment in the workplace can build a healthy work ecosystem that increases the productivity and efficiency of the organization. Further, enforcing rules related to safety and security can prevent incidents and strengthen resilience.
Fostering Healthy Competition
Regulatory compliance eliminates unfair monopolies that can stifle competition. Complying with such regulations enables fair practices which encourage innovation. Organizations are motivated to offer products and services of superior quality and avoid complacency in design, production, and delivery.
Gaining Better Branding
Adhering to regulatory compliance requirements can help build better public relations as meeting regulatory obligations increases stakeholder confidence. The same can be used in branding and marketing campaigns by communicating the organization’s commitment to compliance processes, ethical codes, and norms.
Reducing Risk and Increasing Profitability
Businesses can reap continued profits when their customer churn is maintained at healthy levels. By following regulatory compliance requirements, customer trust can be sustained. For example, securing customer data against breaches or theft can work as a competitive differentiator. In addition, business partners also appreciate working with an organization that is safe and reliable, resulting in increased synergies and long-lasting partnerships.
What are the Consequences of Non-Compliance and Lapses in Regulatory Compliance?
Non-compliance arises when the business fails to comply with applicable legal obligations. An increasing number of organizations are prioritizing regulatory compliance as a key strategic requirement. In MetricStream’s State of the Compliance Survey Report, 2021, it was found that 64% of organizations intend to focus on enhancing regulatory and internal compliance assessments.
Along with non-compliance, lapses in regulatory compliance can lead to several adverse consequences, such as
Penalties
Penalties, most often monetary, can be one-off or cumulative over a period of time. The penalties for non-compliance are very high, often running into millions of dollars. For example, the fine framework in GDPR can reach a maximum of €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover – whichever is greater – for severe violations. Organizations that willfully violate the law would expose their leaders and management to individual liability and even jail time, in extreme cases.
Business Disruption
Non-compliance could result in the business being suspended or even debarred from bidding on government contracts. Lawsuits and legal actions can disrupt the organization’s operations and may generate additional losses. This can stall manufacturing operations and result in multiple supply chain vulnerabilities. In addition, they can result in security risks such as data breaches, where sensitive and confidential information may be exposed in the public domain due to poor security measures. Compliance violations result in a reduction in business productivity as levies affect business activities and staff. Such violations can even lead to the suspension of business activities in one area or in extreme cases, the entire organization might be shut down due to the suspension of the business license.
Reputation Losses
Non-compliant businesses suffer a loss of reputation among consumers, clients, business partners, and the public due to negative publicity in the media.
The resulting loss of customer confidence and decreased customer churn can lead to a loss in revenues in the long term, lasting several years into the future. The organization may also be subjected to stricter compliance regulations subsequent to an incident, resulting in steadily increasing compliance costs.
What is a Regulatory Compliance Policy?
A regulatory compliance policy is a blueprint based on which an organization draws its compliance practices. It is a declaration of a company, usually in written format, wherein the establishment affirms its compliance and commitment to relevant laws and regulations. It provides necessary details on the procedures and structures created for this purpose such as a regulatory compliance plan and appointment of a compliance officer.
A regulatory compliance policy helps to create a culture of compliance in the organization and is useful in shielding the organization from risk caused by rogue employees. Moreover, given the yearly increase in regulatory information, a regulatory compliance policy acts as a reference to prioritize compliance processes keeping business goals and interests aligned with regulatory compliance.
Leveraging technology for policy and document management helps streamline and simplify the creation and communication of organizational policies, while providing a centralized policy portal to store and access the latest policies.
How is a Regulatory Compliance Policy Formulated?
A regulatory compliance policy can be formulated by considering the following aspects that may vary individually for each organization.
- Understand the context and purpose of the regulatory compliance policy. Is it to decrease compliance risk? Is it to foster communication with stakeholders? Is it to educate employees?
- Determine its scope. To whom and in what capacity does this policy apply? are there any limitations or exceptions to its applications?
- Determine the policy statement by considering the above aspects on purpose and scope. Such a policy statement highlights the guiding principles needed to define all of the decisions and actions related to regulatory compliance.
- Include all the specific actions necessary to commit to regulatory compliance.
- Include all the procedures in place for the same.
- Assign relevant authorities for monitoring and review of regulatory compliance.
- Highlight the documentation and communication protocols.
The contents of the regulatory compliance policy are often overseen by a Chief Compliance Officer in a draft policy, which is then further discussed with various functional heads to determine its application across the organization. Open deliberation and consensus can lead to wider acceptance of the policy in the organization.
Once the policy is considered a final draft, the company’s Board of Directors is responsible for actioning it and ensuring that compliance becomes a necessary discussion during reviews by the Board.
What Role Does a Compliance Officer Play in Implementing Regulatory Compliance Policy?
The compliance officer in an organization handles all compliance-related matters such that the business can manage risk, maintain its reputation and goodwill, and avoid legal consequences. Most importantly, the chief compliance officer is responsible for driving a culture of compliance and integrity.
Depending on the industry, the role of compliance might change in detail but in general, the compliance officer holds the responsibility for setting up and implementing the regulatory compliance policy or program. The compliance officer is usually tasked with
- Carrying out regular audits to assess compliance risk and manage it effectively by working with the management and employees
- Monitoring the regulatory environment and keeping track of changes in compliance requirements and ensuring compliance with the sam
- Acting as the nodal authority for resolving any and all concerns regarding compliance within the organization
- Enforcing disciplinary action in cases of violations of the regulatory compliance policy or program
periodically reviewing existing compliance processes to incorporate best practices and improve regulatory compliance
What are the Best Practices to Ensure Regulatory Compliance?
By following known and accepted best practices, organizations can consistently maintain regulatory compliance.
While not all organizations can have specialized roles such as a full-time compliance officer, the responsibilities for the same can be delegated to existing personnel in appropriate organizational positions and with the support of best-in-class tools.
Here are some general best practices for organizations to follow in ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Stay on top of changes in the regulatory landscape both at the concerned industry level as well as the jurisdiction level.
- Develop and maintain a compliance code of conduct to create a culture of compliance in the workplace, thus encouraging fair and ethical practices.
- Document the compliance processes. This can be done with a clear delineation of the roles and responsibilities of staff involved in compliance management. Such documentation would be valuable during regulatory compliance audits.
- Train employees in regulatory compliance by conducting workshops, training sessions, and periodically assessing them on compliance requirements.
- Periodically review the regulatory compliance policy to correct weaknesses in the policy and to ensure that compliance is up to date with the latest changes in the regulatory environment.
- Automate compliance activities depending on the size and scope of the organization.
How is Regulatory Compliance Different from Corporate Compliance?
Regulatory compliance focuses on aligning with external legal mandates such as laws and regulations in respective jurisdictions or industries. Corporate compliance is internal in nature with processes and procedures aimed at streamlining internal business requirements. Both regulatory compliance and corporate compliance have a common goal—that is ensuring accountability of the business.
Why is it Important to Have a Regulatory Compliance Policy in Place?
Having a regulatory compliance policy is an explicit indicator that the organization is serious about its commitment to regulatory compliance. This is particularly important for large corporations as they have to adhere to numerous regulations within the country at various levels and internationally if they have a global presence.
What are the Challenges of Regulatory Compliance?
Sometimes, regulations in one area can be at cross-purposes with regulations in other areas. For instance, the data privacy regulation where citizens can exercise the ‘right to be forgotten’ can conflict with regulations that mandate organizations to retain the data of users for long durations of time.
Other challenges include predicting the impact of regulatory compliance on the strategic direction of the company as directly measuring the value of compliance can be difficult.
What is Regulatory Compliance Management?
Regulatory compliance management is how an organization systematically secures regulatory compliance by establishing a standard set of processes and procedures,and investing in appropriate technology that align and facilitate visibility into controls while eliminating inefficiencies.
Regulatory compliance is the process of complying with applicable laws, regulations, policies and procedures, standards, and the other rules issued by governments and regulatory bodies like FINRA, SEC, FDA, NERC, Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), etc.
Depending on the industry and jurisdiction, regulations vary significantly. Large organizations with a global footprint need to comply with pertinent laws and regulations in all the countries they operate in, and from. Some industries, such as financial services, information technology (IT), and healthcare, face numerous and often complex regulations and compliance frameworks due to their impact on the economy, business, and health infrastructure respectively. Additionally, many of these industries are also at significant risk of cyber breaches, due to the increasingly complex and evolving cyberattack surface.
As a business grows and expands, the regulations it is subjected to also increase in scale and volume, often becoming complex due to overlapping jurisdictions of multiple authorities. This requires an organization to implement the right measures, policies, and processes to ensure compliance.
This page provides a comprehensive overview of regulatory compliance and its importance, the benefits of regulatory compliance, the consequences of non-compliance, and the best practices to follow to achieve regulatory compliance.
Regulatory Compliance Examples
Some of the major regulatory compliance examples related to financial and non-financial sectors include the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA), and the European Union’s (E.U.) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
Regulatory Requirements
Regulatory requirements are legally binding rules established by government authorities or delegated bodies to control an industry, process, or sector. Organizations must adhere to these requirements to avoid penalties and ensure responsible conduct.
In the US, several laws and regulations are in place to protect various stakeholders, including the business itself.
Compliance laws protect consumers from any harmful consequences of the firm’s operations, help the firm protect its reputation, and help senior management and leadership avoid criminal liability. These laws, regulations, and guidelines are industry-specific and some of them have dedicated oversight bodies that ensure implementation.
For example, the financial industry is governed by legislation including the Dodd-Frank Act and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX). The Dodd-Frank Act was brought into effect in 2010 to facilitate financial stability by augmenting transparency and accountability. Regulatory compliance of banks concerning speculative trading, investment activities, and reserve requirements was tightened as a direct consequence of this Act. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) was created to protect stakeholders of publicly traded companies from fraudulent accounting and financial practices. SOX regulates the activities of corporations, such as the certification of financial reports and corporate record-keeping.
Further, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) was created to safeguard the data and interests of people covered through health insurance and governs the storage and privacy of their personal medical information and data. Legislations such as HIPAA further serve as a starting point for instituting a comprehensive cybersecurity program in place.
Major regulatory agencies in the US include:
- The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) An independent agency that enforces antitrust laws which are non-criminal for establishing a competitive market and protecting consumers from deceitful business practices.
- The Occupational Health & Safety Administration (OSHA) This body regulates working conditions by preparing and enforcing standards to provide a safe and healthy workplace.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) The FDA regulates companies that are involved in manufacturing food products, cosmetic products, and drugs. Its regulatory powers also extend to the manufacturers of medical devices.
- National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) It is a non-regulatory agency that develops standards and guidelines to help meet specific regulatory compliance requirements such as IT and data security.
The European Union is a supranational entity and therefore its regulations apply to all its member countries. It established the European Systemic Risk Board (ESRB) for financial supervision and has independent entities such as the European Banking Authority (EBA) and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) which set up technical standards.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) includes regulations that apply to organizations collecting data from EU citizens irrespective of the location of the organization. Further, GDPR applies to the data storage of residents within the EU even if they are not EU citizens.
Countries outside the EU in Europe such as the United Kingdom have their own regulatory compliance frameworks and authorities such as the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) to preserve market integrity.
While mandates of regulatory compliance differ from country to country, similar laws to SOX exist in various countries such as the Corporate Law Economic Reform Program Act 2004 (CLERP 9) of Australia and Deutscher Corporate Governance Kodex (DCGK) of Germany.
In Canada, unlike the majority of countries, there is no federal regulatory agency for securities. Agencies within the provinces and other territories collaborate to regulate trading in securities.
Regulatory compliance is important to uphold the integrity of business processes, protecting public interest as well as stakeholder interest. It ensures that businesses operate fairly and ethically. When businesses are open and transparent about their regulatory compliance mechanisms, trust and goodwill among clients and business partners increase. This can, over time, improve brand perception and increase the overall profitability of the organization.
With good regulation, consumers are protected from harmful and fraudulent actions taken by business entities such as predatory mortgage lending, which led to the subprime mortgage crisis of 2008. At the same time, directors and managers of businesses that follow regulatory compliance can steer clear of criminal liability and premature career termination due to actions that they may be held directly responsible for.
Additionally, formulating a solid regulatory compliance strategy helps organizations stay on top of risks by being future-ready.
Organizations that maintain consistent regulatory compliance management can reap significant benefits and outcomes both in the short term and over an extended period of time. Important benefits include

Avoiding Unnecessary Legal Issues
Regulatory compliance frameworks ensure that all necessary legal obligations are met. For example, industries that require the collection and storage of large amounts of user data can avoid legal issues by following regulations such as GDPR. The cost of compliance, as a result, is much lower than non-compliance.
Increasing Efficiency and Safety in the Workplace
Implementation of rules against discrimination and harassment in the workplace can build a healthy work ecosystem that increases the productivity and efficiency of the organization. Further, enforcing rules related to safety and security can prevent incidents and strengthen resilience.
Fostering Healthy Competition
Regulatory compliance eliminates unfair monopolies that can stifle competition. Complying with such regulations enables fair practices which encourage innovation. Organizations are motivated to offer products and services of superior quality and avoid complacency in design, production, and delivery.
Gaining Better Branding
Adhering to regulatory compliance requirements can help build better public relations as meeting regulatory obligations increases stakeholder confidence. The same can be used in branding and marketing campaigns by communicating the organization’s commitment to compliance processes, ethical codes, and norms.
Reducing Risk and Increasing Profitability
Businesses can reap continued profits when their customer churn is maintained at healthy levels. By following regulatory compliance requirements, customer trust can be sustained. For example, securing customer data against breaches or theft can work as a competitive differentiator. In addition, business partners also appreciate working with an organization that is safe and reliable, resulting in increased synergies and long-lasting partnerships.
Non-compliance arises when the business fails to comply with applicable legal obligations. An increasing number of organizations are prioritizing regulatory compliance as a key strategic requirement. In MetricStream’s State of the Compliance Survey Report, 2021, it was found that 64% of organizations intend to focus on enhancing regulatory and internal compliance assessments.
Along with non-compliance, lapses in regulatory compliance can lead to several adverse consequences, such as
Penalties
Penalties, most often monetary, can be one-off or cumulative over a period of time. The penalties for non-compliance are very high, often running into millions of dollars. For example, the fine framework in GDPR can reach a maximum of €20 million or 4% of annual global turnover – whichever is greater – for severe violations. Organizations that willfully violate the law would expose their leaders and management to individual liability and even jail time, in extreme cases.
Business Disruption
Non-compliance could result in the business being suspended or even debarred from bidding on government contracts. Lawsuits and legal actions can disrupt the organization’s operations and may generate additional losses. This can stall manufacturing operations and result in multiple supply chain vulnerabilities. In addition, they can result in security risks such as data breaches, where sensitive and confidential information may be exposed in the public domain due to poor security measures. Compliance violations result in a reduction in business productivity as levies affect business activities and staff. Such violations can even lead to the suspension of business activities in one area or in extreme cases, the entire organization might be shut down due to the suspension of the business license.
Reputation Losses
Non-compliant businesses suffer a loss of reputation among consumers, clients, business partners, and the public due to negative publicity in the media.
The resulting loss of customer confidence and decreased customer churn can lead to a loss in revenues in the long term, lasting several years into the future. The organization may also be subjected to stricter compliance regulations subsequent to an incident, resulting in steadily increasing compliance costs.
A regulatory compliance policy is a blueprint based on which an organization draws its compliance practices. It is a declaration of a company, usually in written format, wherein the establishment affirms its compliance and commitment to relevant laws and regulations. It provides necessary details on the procedures and structures created for this purpose such as a regulatory compliance plan and appointment of a compliance officer.
A regulatory compliance policy helps to create a culture of compliance in the organization and is useful in shielding the organization from risk caused by rogue employees. Moreover, given the yearly increase in regulatory information, a regulatory compliance policy acts as a reference to prioritize compliance processes keeping business goals and interests aligned with regulatory compliance.
Leveraging technology for policy and document management helps streamline and simplify the creation and communication of organizational policies, while providing a centralized policy portal to store and access the latest policies.
A regulatory compliance policy can be formulated by considering the following aspects that may vary individually for each organization.
- Understand the context and purpose of the regulatory compliance policy. Is it to decrease compliance risk? Is it to foster communication with stakeholders? Is it to educate employees?
- Determine its scope. To whom and in what capacity does this policy apply? are there any limitations or exceptions to its applications?
- Determine the policy statement by considering the above aspects on purpose and scope. Such a policy statement highlights the guiding principles needed to define all of the decisions and actions related to regulatory compliance.
- Include all the specific actions necessary to commit to regulatory compliance.
- Include all the procedures in place for the same.
- Assign relevant authorities for monitoring and review of regulatory compliance.
- Highlight the documentation and communication protocols.
The contents of the regulatory compliance policy are often overseen by a Chief Compliance Officer in a draft policy, which is then further discussed with various functional heads to determine its application across the organization. Open deliberation and consensus can lead to wider acceptance of the policy in the organization.
Once the policy is considered a final draft, the company’s Board of Directors is responsible for actioning it and ensuring that compliance becomes a necessary discussion during reviews by the Board.
The compliance officer in an organization handles all compliance-related matters such that the business can manage risk, maintain its reputation and goodwill, and avoid legal consequences. Most importantly, the chief compliance officer is responsible for driving a culture of compliance and integrity.
Depending on the industry, the role of compliance might change in detail but in general, the compliance officer holds the responsibility for setting up and implementing the regulatory compliance policy or program. The compliance officer is usually tasked with
- Carrying out regular audits to assess compliance risk and manage it effectively by working with the management and employees
- Monitoring the regulatory environment and keeping track of changes in compliance requirements and ensuring compliance with the sam
- Acting as the nodal authority for resolving any and all concerns regarding compliance within the organization
- Enforcing disciplinary action in cases of violations of the regulatory compliance policy or program
periodically reviewing existing compliance processes to incorporate best practices and improve regulatory compliance
By following known and accepted best practices, organizations can consistently maintain regulatory compliance.
While not all organizations can have specialized roles such as a full-time compliance officer, the responsibilities for the same can be delegated to existing personnel in appropriate organizational positions and with the support of best-in-class tools.
Here are some general best practices for organizations to follow in ensuring regulatory compliance.
- Stay on top of changes in the regulatory landscape both at the concerned industry level as well as the jurisdiction level.
- Develop and maintain a compliance code of conduct to create a culture of compliance in the workplace, thus encouraging fair and ethical practices.
- Document the compliance processes. This can be done with a clear delineation of the roles and responsibilities of staff involved in compliance management. Such documentation would be valuable during regulatory compliance audits.
- Train employees in regulatory compliance by conducting workshops, training sessions, and periodically assessing them on compliance requirements.
- Periodically review the regulatory compliance policy to correct weaknesses in the policy and to ensure that compliance is up to date with the latest changes in the regulatory environment.
- Automate compliance activities depending on the size and scope of the organization.
Regulatory compliance focuses on aligning with external legal mandates such as laws and regulations in respective jurisdictions or industries. Corporate compliance is internal in nature with processes and procedures aimed at streamlining internal business requirements. Both regulatory compliance and corporate compliance have a common goal—that is ensuring accountability of the business.
Having a regulatory compliance policy is an explicit indicator that the organization is serious about its commitment to regulatory compliance. This is particularly important for large corporations as they have to adhere to numerous regulations within the country at various levels and internationally if they have a global presence.
Sometimes, regulations in one area can be at cross-purposes with regulations in other areas. For instance, the data privacy regulation where citizens can exercise the ‘right to be forgotten’ can conflict with regulations that mandate organizations to retain the data of users for long durations of time.
Other challenges include predicting the impact of regulatory compliance on the strategic direction of the company as directly measuring the value of compliance can be difficult.
Regulatory compliance management is how an organization systematically secures regulatory compliance by establishing a standard set of processes and procedures,and investing in appropriate technology that align and facilitate visibility into controls while eliminating inefficiencies.








