Introduction
Managing risk stands as a fundamental pillar in safeguarding a company's trajectory towards success and resilience. This complex undertaking involves deciphering and prioritizing a multitude of risks that can derail an organization's objectives.
The stakes are high, as underscored by a survey from the Global Risk Management Survey, Ninth Edition by Aon, revealing that 82% of their respondents acknowledge they are actively engaged in some form of risk management. This highlights the ubiquitous nature of risk across sectors and the immediate need for efficient methodologies in risk identification and prioritization.
In today’s volatile environment, risk is a constant undercurrent. According to the 2025 Aon Global Risk Management Survey, cyber attacks, supply-chain disruptions, and geopolitical volatility remain among the top global risks, underscoring the urgency for better risk visibility and prioritization.
That’s why many choose a tool like MetricStream. Its platform gathers risk data from across the organisation and turns it into interactive heatmaps that highlight key exposures at a glance. Teams can see where risks cluster, what’s changing, and where to act first — helping them stay ahead, not just react.
With effective heatmaps, organisations avoid surprises and stay prepared. They make it easier for leaders to see risk at scale, talk about it clearly, and match resources to what matters most.
Key Takeaways
- A risk heat map is a visual tool that represents the likelihood and impact of various risks on a color-coded grid, helping organizations prioritize and manage potential threats effectively.
- Purpose of Risk Heat Maps: Visual tools to prioritize and manage risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Creation Process: Identify and assess risks, assign scores for likelihood and impact, plot on a grid, use color-coding for severity, and develop mitigation strategies.
- Key Benefits: Enhanced visualization, improved stakeholder communication, proactive risk management, increased organizational risk awareness, and strengthened analytical capabilities.
- Importance of Regular Updates: Regular reviews and updates ensure the heat map remains an accurate and effective tool.
What is a Risk Heat Map?
A risk heat map is a visual tool that organizes risks based on their likelihood and impact, allowing teams to understand exposure at a glance. It brings together data from assessments, controls, and incidents to present a clear view of where risks concentrate and which areas need attention. By translating risk levels into a simple color-coded grid, it helps leaders prioritise actions and make informed decisions.
Components of a Risk Heat Map
Central to the effectiveness of a risk heat map are its two primary axes, one representing the likelihood or probability of a risk occurring, and the other showcasing the impact or severity of consequences should the risk materialize. This two-dimensional framework allows for a nuanced analysis of risks, categorizing them by both, their potential to happen, and also by the magnitude of their possible effects on the organization.
Adding a layer of intuitive understanding to this framework, color coding enhances the heat map’s accuracy.
Traditionally, this involves employing a color gradient – typically red, yellow, and green – to signify the severity of risks. Risks mapped in red zones are indicative of critical threats that demand immediate attention due to their high probability and significant impact.
Yellow, on the other hand, signals moderate risks that warrant caution but may not require urgent action. Green areas are associated with low-priority risks, either due to their low likelihood, minimal impact, or both.
This color-coded system simplifies complex risk assessments, allowing stakeholders to quickly grasp and navigate the situation.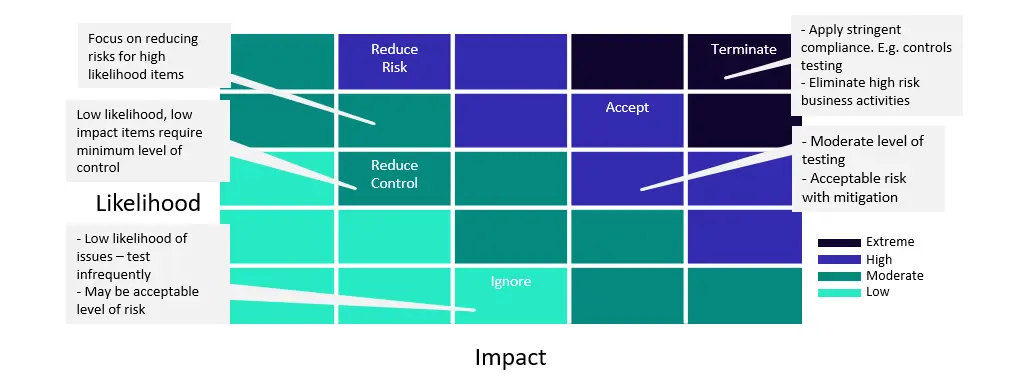
Figure 1: Risk Heat Map
How Does A Risk Heat Map Work?
A risk heat map works by turning raw risk information into a visual layout that helps teams see where attention is needed most. Here’s how the process comes together:
Collect the inputs that matter
Start with a list of risks and pull in data from incidents, assessments, audits, and subject-matter insights. The map reflects the quality of the information fed into it.
Score likelihood and impact using shared criteria
Agree on simple scoring scales and define what each score means. When teams use the same language, the comparisons become fair and consistent.
Place each risk on the grid
Plot risks based on their likelihood (horizontal axis) and their impact (vertical axis). The placement shows which risks sit in the high-priority zones and which ones require routine monitoring.
Use colours to highlight priority levels
Colour coding helps teams understand severity at a glance. High-risk clusters stand out immediately, making conversations faster and more focused.
Drill into the details behind each risk
A good heat map lets users click into a cell to see the controls, ownership, past incidents, and open actions tied to that risk. This turns the visual into a working tool, not a static snapshot.
Review and update the map regularly
Risk profiles shift as controls change, new threats emerge, or the business expands. Regular refresh cycles keep the map current and trustworthy.
Link the heat map to decisions and actions
The map becomes valuable when it guides next steps—whether it’s allocating budget, adjusting controls, or escalating issues to leadership. It should support judgment, not replace it.
Watch for blind spots
Heat maps simplify complex information, but they can hide uncertainty. Teams should question weak data, revisit assumptions, and avoid over-relying on perfect-looking grids.
Benefits of Using A Risk Heat Map
Using a risk heat map enhances risk management by visualizing complex data in a color-coded matrix. It improves communication among stakeholders, enables proactive risk mitigation, raises risk awareness across the organization, and enhances analytical capabilities through comprehensive data analysis.
Below are detailed insights into some key advantages of incorporating risk heat maps into an organization’s risk management strategy.
Enhanced Visualization of Complex Risk Profiles
These maps transform the daunting complexity of risk data into an accessible, color-coded matrix. This visualization lays bare the terrain of risks scattered across the organization, categorized by severity and likelihood. The clear demarcation of risk levels facilitates a deeper understanding among all organizational levels, making it immediately apparent which areas require urgent attention and which pose less of a threat.
Strengthened Communication with Stakeholders
When discussing risks, the abstract can swiftly become concrete through the use of these maps. They serve as a shared language among various stakeholders, transcending the barriers of technical jargon. Executives, board members, and operational teams can all converge on this common ground, fostering a unified understanding and approach to risk management. This collaborative approach is crucial for aligning risk mitigation efforts with organizational goals.
Facilitation of Proactive Risk Management
By highlighting potential high-impact risks before they manifest, organizations are afforded the precious commodity of time — time to strategize, time to allocate appropriate resources, and time to implement measures that can either prevent the occurrence of a risk or significantly mitigate its impact. This proactive approach helps preserve organizational resources and also safeguards against the potential derailment of business objectives.
Improved Risk Awareness Across the Organization
The visual and easy-to-understand nature of heat maps makes them accessible to employees at all levels, fostering a culture of risk awareness and responsibility. When everyone is aware of the potential risks and understands their impact, it fosters a collective effort towards risk mitigation. This widespread awareness is vital for ensuring that risk management becomes an integral part of the organizational culture, rather than being viewed as a separate or external process.
Enhanced Analytical Capabilities
The process of creating a risk heat map requires gathering, analysis, and synthesis of complex risk data. This exercise enhances the organization’s analytical capabilities as it involves evaluating risks from multiple dimensions, including likelihood, impact, and velocity. By engaging in this analytical process, organizations can uncover insights that might have been overlooked otherwise. These insights can then inform more strategic risk management approaches and contribute to a deeper understanding of the organization’s risk profile.
When To Use a Risk Heat Map
Use a heat map in these situations:
Strategic planning
When leaders set goals or consider new markets, a heat map shows which risks could block plans and where mitigation will matter most.
Project kickoffs and major initiatives
Before launching large programs, map risks to spot critical dependencies, resource needs, and controls that must be in place from day one.
Quarterly or annual risk reviews
Use the map to summarize changes across the organisation, show trending exposures, and guide which risks deserve deeper attention each cycle.
Incident reviews and root-cause analysis
After a breach or failure, plotting related risks helps reveal weak links, control gaps, and the true scope of impact.
Board and executive reporting
A visual heat map turns complex risk data into a conversation tool that helps boards quickly grasp priority areas and decide on resources.
Vendor and third-party risk assessments
When evaluating suppliers, heat maps help compare which providers introduce the most exposure and where contractual controls are needed.
Regulatory or compliance changes
If rules shift, use a heat map to see which processes or controls will be affected and to prioritise remediation work.
How To Create a Risk Heat Map
Here are the key steps involved in its creation:
Identification of Risks:
The first step is to list all possible risks that can affect the organization. This stage requires thorough brainstorming and input from various departments to ensure no potential risk is overlooked.
Risk Assessment:
Each identified risk undergoes a comprehensive assessment to determine its likelihood of occurrence and the potential impact on the organization. These assessments are typically quantitative, assigning scores to both likelihood and impact on a predetermined scale.
Data Compilation:
The likelihood and impact scores gathered from risk assessments are pivotal data points. They are meticulously compiled and serve as the foundational input for populating the heat map.
Plotting on the Heat Map:
With the data in hand, each risk is plotted on the heat map according to its likelihood and impact scores. The axes of the heat map represent these two dimensions.
Visualization Through Colors:
The heat map uses a color gradient to represent the severity of risks. The most widely used gradient is the red, yellow, and green gradient, with green signifying low-priority risks, yellow indicating moderate-priority risks, and red highlighting high-priority or critical risks. Critical risks require immediate attention as they pose the most significant threat to the organization's objectives. This visual representation makes it intuitive to understand the risk landscape at a glance.
Develop Mitigation Strategies:
For the highest-priority risks, create detailed mitigation plans outlining specific actions to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. Assign responsibilities and set timelines for implementing these strategies.
Review and Update Regularly:
A risk heat map is a dynamic tool that should be reviewed and updated regularly. As new risks emerge and existing risks change, adjust the heat map accordingly to ensure it remains an accurate representation of the current risk landscape.
Conclusion
The construction and utilization of a risk heat map are indispensable practices when it comes to managing operational workflows. While the process may seem complex, the benefits of implementing a risk heat map are profound, offering clarity in the often murky waters of risk management.
MetricStream's offering is designed to support organizations in this journey, providing a foundation upon which they can build a robust risk management framework that is both resilient and responsive to changes in their operational environment. MetricStream BusinessGRC software solutions provide real-time information on risk management programs across the organization through role-based landing pages, powerful dashboards with scorecards, risk heat maps, enhanced charting capabilities, intuitive reports, and more. These features help improve enterprise-wide transparency in the risk management process and highlight issues that need to be addressed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are risk heat maps important?
Risk heat maps are important because they provide a clear and immediate visual representation of risk levels, allowing organizations to focus resources on addressing the most significant risks.
How is risk scored on a heat map?
Risks are scored based on their likelihood and impact, typically using a consistent scale (e.g., 1 to 5). These scores are then combined to determine the overall risk level, which is plotted on the heat map.
How often should a risk heat map be updated?
A risk heat map should be updated regularly, such as quarterly or whenever significant changes occur in the organization’s risk environment, to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
What is a Risk Heat Map?
A risk heat map is a visual tool that displays risks based on their likelihood and impact, helping organizations quickly assess and prioritize threats.
Why and When Should You Use a Risk Heat Map?
You should use a risk heat map when evaluating potential threats to gain clarity, prioritize responses, and guide resource allocation.
How Does a Risk Heat Map Work?
It works by plotting risks on a matrix, usually with likelihood on one axis and impact on the other, using color coding to highlight severity levels.
How Do You Create a Risk Heat Map?
Identify risks, assess their likelihood and impact, assign scores, and plot them on a matrix with color coding to visualize critical areas.
What Are the Key Components of a Risk Heat Map?
Key components include the likelihood scale, impact scale, color coding, risk categories, and plotted risks with their severity levels.
Managing risk stands as a fundamental pillar in safeguarding a company's trajectory towards success and resilience. This complex undertaking involves deciphering and prioritizing a multitude of risks that can derail an organization's objectives.
The stakes are high, as underscored by a survey from the Global Risk Management Survey, Ninth Edition by Aon, revealing that 82% of their respondents acknowledge they are actively engaged in some form of risk management. This highlights the ubiquitous nature of risk across sectors and the immediate need for efficient methodologies in risk identification and prioritization.
In today’s volatile environment, risk is a constant undercurrent. According to the 2025 Aon Global Risk Management Survey, cyber attacks, supply-chain disruptions, and geopolitical volatility remain among the top global risks, underscoring the urgency for better risk visibility and prioritization.
That’s why many choose a tool like MetricStream. Its platform gathers risk data from across the organisation and turns it into interactive heatmaps that highlight key exposures at a glance. Teams can see where risks cluster, what’s changing, and where to act first — helping them stay ahead, not just react.
With effective heatmaps, organisations avoid surprises and stay prepared. They make it easier for leaders to see risk at scale, talk about it clearly, and match resources to what matters most.
- A risk heat map is a visual tool that represents the likelihood and impact of various risks on a color-coded grid, helping organizations prioritize and manage potential threats effectively.
- Purpose of Risk Heat Maps: Visual tools to prioritize and manage risks based on their likelihood and impact.
- Creation Process: Identify and assess risks, assign scores for likelihood and impact, plot on a grid, use color-coding for severity, and develop mitigation strategies.
- Key Benefits: Enhanced visualization, improved stakeholder communication, proactive risk management, increased organizational risk awareness, and strengthened analytical capabilities.
- Importance of Regular Updates: Regular reviews and updates ensure the heat map remains an accurate and effective tool.
A risk heat map is a visual tool that organizes risks based on their likelihood and impact, allowing teams to understand exposure at a glance. It brings together data from assessments, controls, and incidents to present a clear view of where risks concentrate and which areas need attention. By translating risk levels into a simple color-coded grid, it helps leaders prioritise actions and make informed decisions.
Central to the effectiveness of a risk heat map are its two primary axes, one representing the likelihood or probability of a risk occurring, and the other showcasing the impact or severity of consequences should the risk materialize. This two-dimensional framework allows for a nuanced analysis of risks, categorizing them by both, their potential to happen, and also by the magnitude of their possible effects on the organization.
Adding a layer of intuitive understanding to this framework, color coding enhances the heat map’s accuracy.
Traditionally, this involves employing a color gradient – typically red, yellow, and green – to signify the severity of risks. Risks mapped in red zones are indicative of critical threats that demand immediate attention due to their high probability and significant impact.
Yellow, on the other hand, signals moderate risks that warrant caution but may not require urgent action. Green areas are associated with low-priority risks, either due to their low likelihood, minimal impact, or both.
This color-coded system simplifies complex risk assessments, allowing stakeholders to quickly grasp and navigate the situation.
Figure 1: Risk Heat Map
A risk heat map works by turning raw risk information into a visual layout that helps teams see where attention is needed most. Here’s how the process comes together:
Collect the inputs that matter
Start with a list of risks and pull in data from incidents, assessments, audits, and subject-matter insights. The map reflects the quality of the information fed into it.
Score likelihood and impact using shared criteria
Agree on simple scoring scales and define what each score means. When teams use the same language, the comparisons become fair and consistent.
Place each risk on the grid
Plot risks based on their likelihood (horizontal axis) and their impact (vertical axis). The placement shows which risks sit in the high-priority zones and which ones require routine monitoring.
Use colours to highlight priority levels
Colour coding helps teams understand severity at a glance. High-risk clusters stand out immediately, making conversations faster and more focused.
Drill into the details behind each risk
A good heat map lets users click into a cell to see the controls, ownership, past incidents, and open actions tied to that risk. This turns the visual into a working tool, not a static snapshot.
Review and update the map regularly
Risk profiles shift as controls change, new threats emerge, or the business expands. Regular refresh cycles keep the map current and trustworthy.
Link the heat map to decisions and actions
The map becomes valuable when it guides next steps—whether it’s allocating budget, adjusting controls, or escalating issues to leadership. It should support judgment, not replace it.
Watch for blind spots
Heat maps simplify complex information, but they can hide uncertainty. Teams should question weak data, revisit assumptions, and avoid over-relying on perfect-looking grids.
Using a risk heat map enhances risk management by visualizing complex data in a color-coded matrix. It improves communication among stakeholders, enables proactive risk mitigation, raises risk awareness across the organization, and enhances analytical capabilities through comprehensive data analysis.
Below are detailed insights into some key advantages of incorporating risk heat maps into an organization’s risk management strategy.
Enhanced Visualization of Complex Risk Profiles
These maps transform the daunting complexity of risk data into an accessible, color-coded matrix. This visualization lays bare the terrain of risks scattered across the organization, categorized by severity and likelihood. The clear demarcation of risk levels facilitates a deeper understanding among all organizational levels, making it immediately apparent which areas require urgent attention and which pose less of a threat.
Strengthened Communication with Stakeholders
When discussing risks, the abstract can swiftly become concrete through the use of these maps. They serve as a shared language among various stakeholders, transcending the barriers of technical jargon. Executives, board members, and operational teams can all converge on this common ground, fostering a unified understanding and approach to risk management. This collaborative approach is crucial for aligning risk mitigation efforts with organizational goals.
Facilitation of Proactive Risk Management
By highlighting potential high-impact risks before they manifest, organizations are afforded the precious commodity of time — time to strategize, time to allocate appropriate resources, and time to implement measures that can either prevent the occurrence of a risk or significantly mitigate its impact. This proactive approach helps preserve organizational resources and also safeguards against the potential derailment of business objectives.
Improved Risk Awareness Across the Organization
The visual and easy-to-understand nature of heat maps makes them accessible to employees at all levels, fostering a culture of risk awareness and responsibility. When everyone is aware of the potential risks and understands their impact, it fosters a collective effort towards risk mitigation. This widespread awareness is vital for ensuring that risk management becomes an integral part of the organizational culture, rather than being viewed as a separate or external process.
Enhanced Analytical Capabilities
The process of creating a risk heat map requires gathering, analysis, and synthesis of complex risk data. This exercise enhances the organization’s analytical capabilities as it involves evaluating risks from multiple dimensions, including likelihood, impact, and velocity. By engaging in this analytical process, organizations can uncover insights that might have been overlooked otherwise. These insights can then inform more strategic risk management approaches and contribute to a deeper understanding of the organization’s risk profile.
Use a heat map in these situations:
Strategic planning
When leaders set goals or consider new markets, a heat map shows which risks could block plans and where mitigation will matter most.
Project kickoffs and major initiatives
Before launching large programs, map risks to spot critical dependencies, resource needs, and controls that must be in place from day one.
Quarterly or annual risk reviews
Use the map to summarize changes across the organisation, show trending exposures, and guide which risks deserve deeper attention each cycle.
Incident reviews and root-cause analysis
After a breach or failure, plotting related risks helps reveal weak links, control gaps, and the true scope of impact.
Board and executive reporting
A visual heat map turns complex risk data into a conversation tool that helps boards quickly grasp priority areas and decide on resources.
Vendor and third-party risk assessments
When evaluating suppliers, heat maps help compare which providers introduce the most exposure and where contractual controls are needed.
Regulatory or compliance changes
If rules shift, use a heat map to see which processes or controls will be affected and to prioritise remediation work.
Here are the key steps involved in its creation:
Identification of Risks:
The first step is to list all possible risks that can affect the organization. This stage requires thorough brainstorming and input from various departments to ensure no potential risk is overlooked.
Risk Assessment:
Each identified risk undergoes a comprehensive assessment to determine its likelihood of occurrence and the potential impact on the organization. These assessments are typically quantitative, assigning scores to both likelihood and impact on a predetermined scale.
Data Compilation:
The likelihood and impact scores gathered from risk assessments are pivotal data points. They are meticulously compiled and serve as the foundational input for populating the heat map.
Plotting on the Heat Map:
With the data in hand, each risk is plotted on the heat map according to its likelihood and impact scores. The axes of the heat map represent these two dimensions.
Visualization Through Colors:
The heat map uses a color gradient to represent the severity of risks. The most widely used gradient is the red, yellow, and green gradient, with green signifying low-priority risks, yellow indicating moderate-priority risks, and red highlighting high-priority or critical risks. Critical risks require immediate attention as they pose the most significant threat to the organization's objectives. This visual representation makes it intuitive to understand the risk landscape at a glance.
Develop Mitigation Strategies:
For the highest-priority risks, create detailed mitigation plans outlining specific actions to reduce the likelihood or impact of the risk. Assign responsibilities and set timelines for implementing these strategies.
Review and Update Regularly:
A risk heat map is a dynamic tool that should be reviewed and updated regularly. As new risks emerge and existing risks change, adjust the heat map accordingly to ensure it remains an accurate representation of the current risk landscape.
The construction and utilization of a risk heat map are indispensable practices when it comes to managing operational workflows. While the process may seem complex, the benefits of implementing a risk heat map are profound, offering clarity in the often murky waters of risk management.
MetricStream's offering is designed to support organizations in this journey, providing a foundation upon which they can build a robust risk management framework that is both resilient and responsive to changes in their operational environment. MetricStream BusinessGRC software solutions provide real-time information on risk management programs across the organization through role-based landing pages, powerful dashboards with scorecards, risk heat maps, enhanced charting capabilities, intuitive reports, and more. These features help improve enterprise-wide transparency in the risk management process and highlight issues that need to be addressed.
Why are risk heat maps important?
Risk heat maps are important because they provide a clear and immediate visual representation of risk levels, allowing organizations to focus resources on addressing the most significant risks.
How is risk scored on a heat map?
Risks are scored based on their likelihood and impact, typically using a consistent scale (e.g., 1 to 5). These scores are then combined to determine the overall risk level, which is plotted on the heat map.
How often should a risk heat map be updated?
A risk heat map should be updated regularly, such as quarterly or whenever significant changes occur in the organization’s risk environment, to ensure it remains relevant and accurate.
What is a Risk Heat Map?
A risk heat map is a visual tool that displays risks based on their likelihood and impact, helping organizations quickly assess and prioritize threats.
Why and When Should You Use a Risk Heat Map?
You should use a risk heat map when evaluating potential threats to gain clarity, prioritize responses, and guide resource allocation.
How Does a Risk Heat Map Work?
It works by plotting risks on a matrix, usually with likelihood on one axis and impact on the other, using color coding to highlight severity levels.
How Do You Create a Risk Heat Map?
Identify risks, assess their likelihood and impact, assign scores, and plot them on a matrix with color coding to visualize critical areas.
What Are the Key Components of a Risk Heat Map?
Key components include the likelihood scale, impact scale, color coding, risk categories, and plotted risks with their severity levels.








