Introduction
Organizations today are required to comply with relevant laws, regulations, and standards at all times. However, this is easier said than done as regulatory requirements are increasing at an unprecedented rate.
As a result, organizations are spending a large amount of time and effort in understanding these regulatory requirements and obligations, mapping them to internal controls and policies, testing the internal controls, identifying issues, tracking remediation, compiling and cataloging evidence, implementing change control, and managing the entire process.
So while compliance is necessary, the costs can quickly add up and impact an organization’s bottom line. With the right strategies, organizations can gain control and visibility over their compliance costs. Taming this budget beast is possible when compliance teams leverage technology, optimize processes, and stay on top of an ever-changing regulatory environment. With the right data and discipline, organizations can transform compliance from a cost center into a great opportunity.
In 2025, organizations face unprecedented regulatory pressures, making compliance increasingly costly. New regulatory fronts such as AI governance, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting, and evolving data privacy laws have added layers of complexity and expense. The rising cost of compliance is a critical concern, with firms navigating a regulatory landscape that demands agility, technology adoption, and rigorous oversight to avoid costly penalties and reputational damage.
Key Takeaways
- Compliance costs are the expenses that an organization incurs to comply with applicable laws, regulations, and standards.
- Traditionally, compliance tasks have been manual, paper-intensive, and time-consuming, requiring significant human intervention at every step. This not only increases the likelihood of errors but also escalates operational costs.
- By leveraging automation tools and digitizing compliance documentation, organizations can streamline workflows, minimize manual labor, and significantly reduce the risk of non-compliance due to human error.
- Once organizations have calculated their compliance costs and identified areas of waste, they should look for ways to simplify and streamline the processes. Even small changes can yield big savings over time.
- Digitization facilitates easier storage, retrieval, and management of compliance documents. Instead of sifting through piles of paper or unorganized digital folders, compliance officers can easily access needed information through a centralized platform, saving time and reducing stress.
What is Compliance Cost?
Compliance costs encompass all expenses incurred to meet legal, regulatory, and standards obligations. These include direct fees and fines, investments in controls and training, system upgrades, and the operational overhead of ongoing monitoring and auditing. Legacy manual approaches intensify these costs and increase error risks, while modern automated solutions enable better cost control, risk reduction, and efficiency improvements.
Companies are realizing that the legacy compliance management approach is excessively resource-intensive and significantly increases the cost of compliance. In addition, it increases the risk of non-compliance, where penalties can be severe.
To ensure a cost-effective way to compliance, organizations need purpose-built software solutions that automate various processes such as regulatory horizon scanning, control testing and monitoring, issue and action management, and reporting while providing comprehensive visibility into the overall compliance posture. This can significantly help them lower their compliance costs, reduce their risk of non-compliance, and free up their personnel to focus on activities that deliver real benefits to the bottom line.
Compliance Costs by the Numbers (2024–2025)
- The average annual compliance cost per organization in the U.S. is approximately $12,800 per employee, reflecting significant investments in regulatory adherence.
- Large financial institutions may spend upwards of $200 million annually on compliance, representing nearly 3% of certain operational expenses.
- Sector-specific average compliance costs vary widely:
- Finance: $150M–$200M annually for large banks
- Healthcare: escalating with tighter patient affordability and transparency mandates, requiring robust financial solutions
- Technology: AI-related compliance with costs averaging €52,227 per AI model annually, factoring certification and governance
- Non-compliance penalties globally surged to $14 billion in 2024, with fines reaching millions per incident in regulated sectors.
- GDPR non-compliance fines can reach up to 4% of annual turnover, with compliance costs from $20,000 to over $100,000 depending on organization size and complexity.
Factors Influencing Compliance Costs
Here are some of the key factors that influence compliance costs:
Complexity of Regulatory Requirements
At the heart of compliance cost lies the complexity of regulatory requirements. Like a tangled skein of yarn, the intricate weave of regulations that organizations must adhere to can be daunting. These requirements aren't static; they evolve, adding layers of complexity for companies to unravel. The more complex the regulations, the more resources and time are required to ensure compliance—be it deciphering legal language, implementing necessary changes, or conducting extensive audits.
Industry-Specific Compliance Challenges
Every industry comes with its own set of compliance hurdles. Financial services, healthcare, and energy sectors, in particular, find themselves under the strictest of regulatory eyes, which significantly shapes their compliance spending. These sectors deal with sensitive data, financial stability, and environmental concerns that necessitate rigorous oversight.
Geographic and Global Regulatory Landscapes
Companies often operate across multiple jurisdictions, each with its own set of regulations. Navigating this landscape adds layers of complexity to compliance efforts. A company based in the United States, for instance, must comply with local laws, but if it does business in Europe, it must also adhere to GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), along with any other regional laws. Managing compliance across diverse regulatory environments requires a nuanced approach and, often, localized expertise, all of which contribute to the overall cost of compliance.
The Pace of Regulatory Change
Lastly, the pace at which regulations change can either inflate or deflate compliance costs. A rapid flurry of regulatory changes requires organizations to be agile, continuously adapting their compliance strategies. This agility, however, does not come cheap.
Staying ahead of the curve requires ongoing investments in training, technology, and sometimes, even restructuring. It's like trying to keep up with a sprint when you are prepared for a marathon; the sudden bursts of speed demand more energy (and resources).
The faster a company can adapt to new or updated regulations, the less disruptive these changes will be to its operations, ultimately influencing compliance costs.
AI and Automation Regulations
The arrival of the EU AI Act and similar global AI governance frameworks introduces costly requirements for algorithm audits, transparency, and documentation. The annual compliance cost for AI models is estimated at around €52,000, with significant certification expenses . Organizations must integrate AI oversight into their compliance programs, raising both strategic and operational costs.
ESG Reporting Pressures
New ESG regulations, such as the EU’s CSRD and the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive, demand detailed environmental and social disclosures, increasing operational and compliance costs. Firms must invest in supply chain transparency and robust reporting to manage regulatory and reputational risks.
Types of Compliance Costs
Here are the various types of compliance costs:
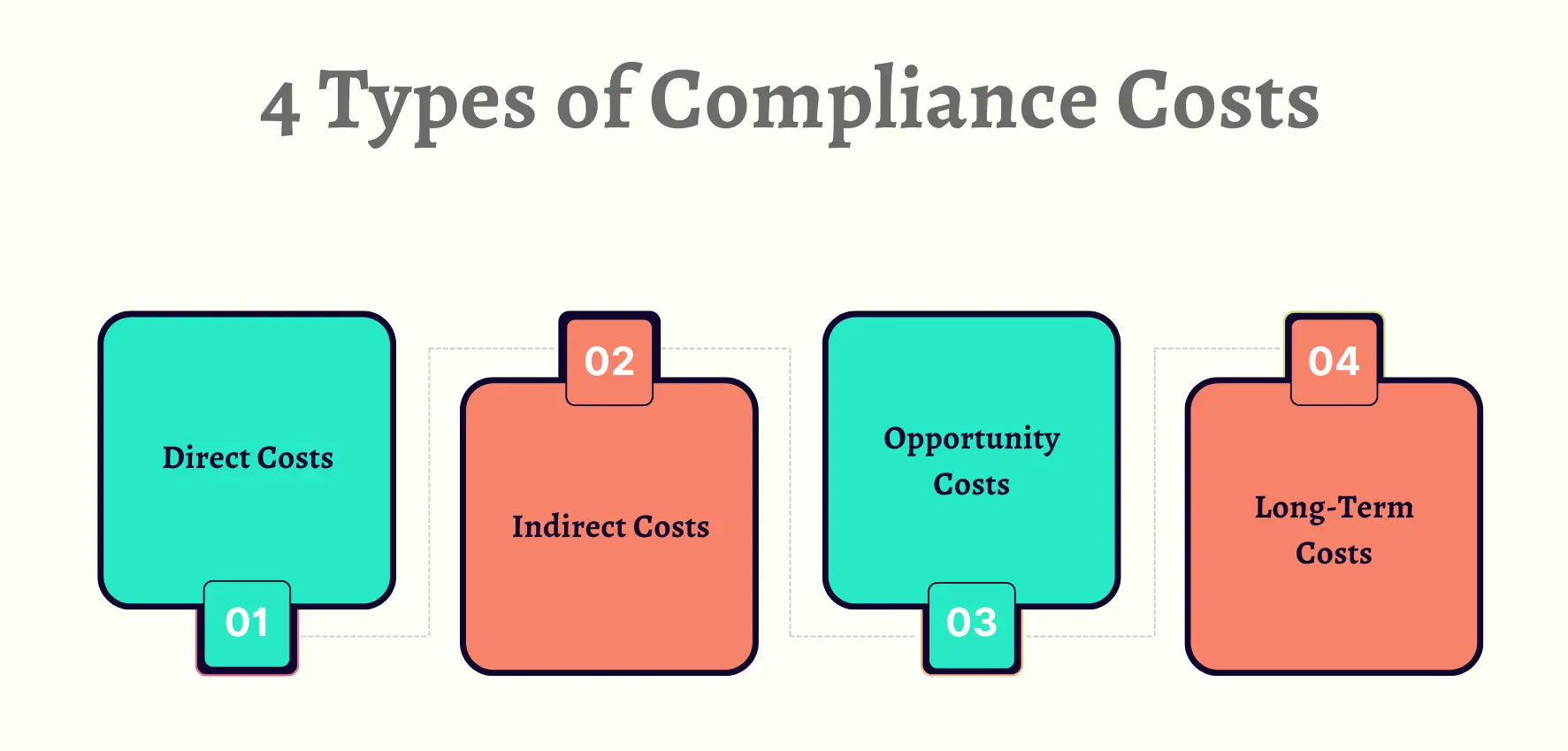
Direct Costs
These costs include fees, fines, and legal expenses that result directly from non-compliance events. For example, if a company fails an audit or violates a regulation, it may face penalties and pay sizable fines. It’ll also likely incur legal fees to address the issue. While these costs are typically unplanned, organizations should budget for potential compliance failures and set aside funds in case issues arise. For instance, breaches under the EU AI Act can cost up to €35 million or 7% of annual turnover; PCI DSS non-compliance can result in fines up to $100,000 per month plus elevated transaction fees.
Indirect Costs
Indirect compliance costs encompass expenses incurred indirectly as a result of compliance activities, such as staff training and system upgrades. Training employees on new regulatory requirements or investing in software upgrades to ensure data security are examples of indirect costs. These costs may not be immediately apparent but are essential for maintaining compliance effectiveness and efficiency over the long term. Failure to invest in staff training or technology upgrades can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and ultimately, increased compliance risks.
Opportunity Costs
Compliance efforts can also incur opportunity costs by diverting resources, time, and attention away from core business activities. For instance, a manufacturing company may allocate significant resources to ensure compliance with safety regulations, potentially limiting its ability to invest in research and development or expansion initiatives.
These opportunity costs represent the value of alternative uses of resources that could have generated additional revenue or competitive advantages if not allocated to compliance activities. Balancing compliance requirements with strategic business objectives is essential for minimizing opportunity costs and maximizing overall organizational performance. For example, financial institutions allocating significant personnel to anti-money laundering compliance could slow innovation.
Long-Term Costs
Long-term compliance costs include the impact on reputation and customer trust resulting from compliance failures. Reputational damage caused by regulatory violations can have lasting consequences, affecting customer loyalty, investor confidence, and brand perception. Rebuilding trust and repairing reputation damage can be costly and time-consuming, which can impact revenue generation and market competitiveness. As such, organizations must consider the potential long-term costs of compliance failures when evaluating the effectiveness of their compliance programs and risk management strategies. Firms with data breaches face multimillion-dollar recovery expenses and long-lasting brand erosion.
Effective Management of Compliance Costs
This journey begins with a clear map and a plan to chart the course through these regulations without draining resources unnecessarily.
Identifying Costs
The first step to managing compliance costs is understanding where they stem from. These costs are not only limited to the direct payments for licenses or fees but extend to the administrative efforts involved in maintaining compliance, training employees, and even the technological solutions implemented.
Budgeting Strategies for Managing Compliance Costs Effectively
Once compliance costs have been identified, the next logical step is to manage them effectively, which involves developing a robust budgeting strategy. The key here is to be as proactive as possible.
Budgeting for compliance should not be an afterthought; it must be an integral part of an organization’s financial planning. This might involve setting aside a fixed percentage of revenue for compliance costs or having a separate compliance fund within the organization’s budget.
To make this process more effective, organizations can also consider historical data. Are certain regulations costing the organization more year after year? Looking back at the compliance costs over the past few years can help identify trends and patterns and forecast future expenses.
Allocating Resources for Ongoing Regulatory Changes
One of the immutable truths about regulatory compliance is that it's always in flux. New regulations can emerge, and existing ones can be revised, which necessitates an agile approach to resource allocation. Here, flexibility is your ally. Allocate resources in a way that can be adjusted as new regulations come into play.
Moreover, adopting a strategic approach to training can significantly reduce costs. Instead of generic, broad-spectrum training, focus on targeted training that addresses the specific regulations that impact your business the most. This ensures your employees are well-equipped to deal with relevant compliance issues without allocating resources toward unnecessary or irrelevant training.
Deploying Regulatory Compliance Solutions
Leveraging regulatory compliance solutions can streamline compliance processes and reduce associated costs. These solutions automate data collection, analysis, and reporting tasks to enhance compliance monitoring, reporting, and risk management while saving time and resources for compliance teams. Capabilities for automated regulatory horizon scanning help organizations stay on top of regulatory changes and proactively adjust their compliance strategies. For example, software that automatically captures relevant regulatory updates ensures that organizations are always working with the most current compliance requirements, eliminating the need for constant manual monitoring.
Compliance Cost Reduction Strategies
While technology-driven solutions are crucial, effectively managing compliance costs also hinges on strategic planning, process improvement, and cultural shifts. Organizations deploying these strategies can achieve substantial cost savings without compromising compliance quality or business agility.
Centralize Compliance Management
Implementing a centralized compliance management system consolidates all compliance-related tasks, data, and documentation into a single platform accessible across departments. This reduces costly redundancies, eliminates inefficiencies from duplicated efforts, and fosters consistent policy enforcement. Centralization enhances visibility into compliance risk areas and facilitates faster decision-making. For example, instead of multiple teams maintaining separate regulatory assessments or audit records, a unified system standardizes processes and streamlines workflows. This consolidation also simplifies managing compliance evidence during audits and inspections, significantly lowering administrative overhead and document retrieval time.
Risk-Based Prioritization
Not all compliance obligations present equal risk or potential penalties. By adopting a risk-based approach, organizations prioritize compliance efforts toward regulations with the greatest impact on business objectives and regulatory exposure. This targeted allocation of resources avoids overextending teams on low-risk requirements, improving overall efficiency.
To implement this, firms conduct thorough risk assessments to categorize compliance tasks based on potential financial, operational, or reputational consequences. Resources, training, and monitoring are then concentrated on critical controls, enabling organizations to address high-stakes areas proactively and cost-effectively.
Regular Compliance Audits with Technology
Although audits are sometimes viewed as a cost center, regular internal audits can generate long-term savings by uncovering gaps and inefficiencies early. Using compliance software automates audit scheduling, data collection, testing, and reporting, reducing manual labor and human error.
Automated audits provide continuous monitoring, real-time alerts for issues, and easy access to audit trails—all of which mitigate the risk of non-compliance penalties. By identifying systemic weaknesses proactively, organizations can implement corrective actions efficiently, preventing costly violations and reputational damage.
Review and Revise Policies
Compliance teams should regularly review organizational policies, standards, and procedures to ensure they remain relevant and efficient. Outdated or redundant policies often create unnecessary compliance burdens and slow down processes.
Streamlining document review workflows and approval chains eliminates bottlenecks, reduces cycle times, and frees personnel from jumping through undue procedural hoops. This simplification drives productivity, enabling the team to focus on value-added compliance activities rather than excessive administrative tasks.
Foster a Genuine Culture of Collaboration
Silos and poor communication create overlaps, gaps, and slow responses that increase compliance costs. Establishing cross-functional teams promotes knowledge sharing and innovative problem-solving, ensuring compliance is integrated into everyday business operations rather than treated as an isolated function.
Organizations benefit from implementing collaboration platforms and encouraging regular cross-departmental interaction, making expertise easily accessible. Smooth, seamless processes enable teams to concentrate on critical compliance risks and strategic initiatives rather than wasting time on redundant or manual tasks.
Additional Best Practices
- Automate Routine Tasks: Using AI and robotic process automation for routine compliance work like data collection, reporting, and monitoring cuts manual input and error risk.
- Training Tailored to Risk Areas: Targeted, role-specific training maximizes impact, reducing unnecessary resource expenditure on broad, irrelevant courses.
- Leverage Predictive Analytics: Analytics tools forecast compliance risk trends and prioritize audits and controls, improving effectiveness and cutting waste.
- Outsource Non-Core Activities: Strategic outsourcing of certain compliance functions (e.g., specialized audit services) can reduce fixed costs and improve scalability.
Compliance Cost Benchmarking Table (2025)
Costs represent averages and may vary widely depending on company size and geographic scope.
How MetricStream Compliance Management Can Help
The MetricStream Compliance Management software helps organizations streamline firm-wide compliance programs with automated workflows and an integrated approach, driving significant time and cost savings. The centralized repository helps align regulations, standards, policies, and controls to provide 360-degree visibility into the compliance posture and eliminate inefficiencies and redundancies. Organizations are able to proactively identify control gaps and weaknesses while powerful dashboards and reports provide real-time insights into compliance processes.
To learn more about MetricStream Compliance Management, request a personalized demo today.
FAQs
What is the average cost of compliance in 2025?
The average U.S. organization spends about $10,000 per employee annually on compliance, with large firms incurring costs in the millions or hundreds of millions, depending on sector and scale.
What industries face the highest compliance costs?
Financial services, healthcare, and technology sectors bear the highest compliance expenses due to stringent regulations and complexity, with finance and healthcare spending up to hundreds of millions annually.
How can automation reduce compliance expenses?
Automation minimizes manual effort, streamlines compliance workflows, reduces risk of human error, and lowers ongoing monitoring and reporting costs, ultimately driving significant savings and operational efficiency.
How do AI regulations affect compliance costs?
AI regulations, such as the EU AI Act, introduce new mandatory requirements including documentation, risk assessments, audits, and certifications. These add substantial annual compliance costs estimated around €52,000 per model and require specialized governance resources.
Organizations today are required to comply with relevant laws, regulations, and standards at all times. However, this is easier said than done as regulatory requirements are increasing at an unprecedented rate.
As a result, organizations are spending a large amount of time and effort in understanding these regulatory requirements and obligations, mapping them to internal controls and policies, testing the internal controls, identifying issues, tracking remediation, compiling and cataloging evidence, implementing change control, and managing the entire process.
So while compliance is necessary, the costs can quickly add up and impact an organization’s bottom line. With the right strategies, organizations can gain control and visibility over their compliance costs. Taming this budget beast is possible when compliance teams leverage technology, optimize processes, and stay on top of an ever-changing regulatory environment. With the right data and discipline, organizations can transform compliance from a cost center into a great opportunity.
In 2025, organizations face unprecedented regulatory pressures, making compliance increasingly costly. New regulatory fronts such as AI governance, ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) reporting, and evolving data privacy laws have added layers of complexity and expense. The rising cost of compliance is a critical concern, with firms navigating a regulatory landscape that demands agility, technology adoption, and rigorous oversight to avoid costly penalties and reputational damage.
- Compliance costs are the expenses that an organization incurs to comply with applicable laws, regulations, and standards.
- Traditionally, compliance tasks have been manual, paper-intensive, and time-consuming, requiring significant human intervention at every step. This not only increases the likelihood of errors but also escalates operational costs.
- By leveraging automation tools and digitizing compliance documentation, organizations can streamline workflows, minimize manual labor, and significantly reduce the risk of non-compliance due to human error.
- Once organizations have calculated their compliance costs and identified areas of waste, they should look for ways to simplify and streamline the processes. Even small changes can yield big savings over time.
- Digitization facilitates easier storage, retrieval, and management of compliance documents. Instead of sifting through piles of paper or unorganized digital folders, compliance officers can easily access needed information through a centralized platform, saving time and reducing stress.
Compliance costs encompass all expenses incurred to meet legal, regulatory, and standards obligations. These include direct fees and fines, investments in controls and training, system upgrades, and the operational overhead of ongoing monitoring and auditing. Legacy manual approaches intensify these costs and increase error risks, while modern automated solutions enable better cost control, risk reduction, and efficiency improvements.
Companies are realizing that the legacy compliance management approach is excessively resource-intensive and significantly increases the cost of compliance. In addition, it increases the risk of non-compliance, where penalties can be severe.
To ensure a cost-effective way to compliance, organizations need purpose-built software solutions that automate various processes such as regulatory horizon scanning, control testing and monitoring, issue and action management, and reporting while providing comprehensive visibility into the overall compliance posture. This can significantly help them lower their compliance costs, reduce their risk of non-compliance, and free up their personnel to focus on activities that deliver real benefits to the bottom line.
- The average annual compliance cost per organization in the U.S. is approximately $12,800 per employee, reflecting significant investments in regulatory adherence.
- Large financial institutions may spend upwards of $200 million annually on compliance, representing nearly 3% of certain operational expenses.
- Sector-specific average compliance costs vary widely:
- Finance: $150M–$200M annually for large banks
- Healthcare: escalating with tighter patient affordability and transparency mandates, requiring robust financial solutions
- Technology: AI-related compliance with costs averaging €52,227 per AI model annually, factoring certification and governance
- Non-compliance penalties globally surged to $14 billion in 2024, with fines reaching millions per incident in regulated sectors.
- GDPR non-compliance fines can reach up to 4% of annual turnover, with compliance costs from $20,000 to over $100,000 depending on organization size and complexity.
Here are some of the key factors that influence compliance costs:
Complexity of Regulatory Requirements
At the heart of compliance cost lies the complexity of regulatory requirements. Like a tangled skein of yarn, the intricate weave of regulations that organizations must adhere to can be daunting. These requirements aren't static; they evolve, adding layers of complexity for companies to unravel. The more complex the regulations, the more resources and time are required to ensure compliance—be it deciphering legal language, implementing necessary changes, or conducting extensive audits.
Industry-Specific Compliance Challenges
Every industry comes with its own set of compliance hurdles. Financial services, healthcare, and energy sectors, in particular, find themselves under the strictest of regulatory eyes, which significantly shapes their compliance spending. These sectors deal with sensitive data, financial stability, and environmental concerns that necessitate rigorous oversight.
Geographic and Global Regulatory Landscapes
Companies often operate across multiple jurisdictions, each with its own set of regulations. Navigating this landscape adds layers of complexity to compliance efforts. A company based in the United States, for instance, must comply with local laws, but if it does business in Europe, it must also adhere to GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), along with any other regional laws. Managing compliance across diverse regulatory environments requires a nuanced approach and, often, localized expertise, all of which contribute to the overall cost of compliance.
The Pace of Regulatory Change
Lastly, the pace at which regulations change can either inflate or deflate compliance costs. A rapid flurry of regulatory changes requires organizations to be agile, continuously adapting their compliance strategies. This agility, however, does not come cheap.
Staying ahead of the curve requires ongoing investments in training, technology, and sometimes, even restructuring. It's like trying to keep up with a sprint when you are prepared for a marathon; the sudden bursts of speed demand more energy (and resources).
The faster a company can adapt to new or updated regulations, the less disruptive these changes will be to its operations, ultimately influencing compliance costs.
AI and Automation Regulations
The arrival of the EU AI Act and similar global AI governance frameworks introduces costly requirements for algorithm audits, transparency, and documentation. The annual compliance cost for AI models is estimated at around €52,000, with significant certification expenses . Organizations must integrate AI oversight into their compliance programs, raising both strategic and operational costs.
ESG Reporting Pressures
New ESG regulations, such as the EU’s CSRD and the Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence Directive, demand detailed environmental and social disclosures, increasing operational and compliance costs. Firms must invest in supply chain transparency and robust reporting to manage regulatory and reputational risks.
Here are the various types of compliance costs:

Direct Costs
These costs include fees, fines, and legal expenses that result directly from non-compliance events. For example, if a company fails an audit or violates a regulation, it may face penalties and pay sizable fines. It’ll also likely incur legal fees to address the issue. While these costs are typically unplanned, organizations should budget for potential compliance failures and set aside funds in case issues arise. For instance, breaches under the EU AI Act can cost up to €35 million or 7% of annual turnover; PCI DSS non-compliance can result in fines up to $100,000 per month plus elevated transaction fees.
Indirect Costs
Indirect compliance costs encompass expenses incurred indirectly as a result of compliance activities, such as staff training and system upgrades. Training employees on new regulatory requirements or investing in software upgrades to ensure data security are examples of indirect costs. These costs may not be immediately apparent but are essential for maintaining compliance effectiveness and efficiency over the long term. Failure to invest in staff training or technology upgrades can lead to inefficiencies, errors, and ultimately, increased compliance risks.
Opportunity Costs
Compliance efforts can also incur opportunity costs by diverting resources, time, and attention away from core business activities. For instance, a manufacturing company may allocate significant resources to ensure compliance with safety regulations, potentially limiting its ability to invest in research and development or expansion initiatives.
These opportunity costs represent the value of alternative uses of resources that could have generated additional revenue or competitive advantages if not allocated to compliance activities. Balancing compliance requirements with strategic business objectives is essential for minimizing opportunity costs and maximizing overall organizational performance. For example, financial institutions allocating significant personnel to anti-money laundering compliance could slow innovation.
Long-Term Costs
Long-term compliance costs include the impact on reputation and customer trust resulting from compliance failures. Reputational damage caused by regulatory violations can have lasting consequences, affecting customer loyalty, investor confidence, and brand perception. Rebuilding trust and repairing reputation damage can be costly and time-consuming, which can impact revenue generation and market competitiveness. As such, organizations must consider the potential long-term costs of compliance failures when evaluating the effectiveness of their compliance programs and risk management strategies. Firms with data breaches face multimillion-dollar recovery expenses and long-lasting brand erosion.
This journey begins with a clear map and a plan to chart the course through these regulations without draining resources unnecessarily.
Identifying Costs
The first step to managing compliance costs is understanding where they stem from. These costs are not only limited to the direct payments for licenses or fees but extend to the administrative efforts involved in maintaining compliance, training employees, and even the technological solutions implemented.
Budgeting Strategies for Managing Compliance Costs Effectively
Once compliance costs have been identified, the next logical step is to manage them effectively, which involves developing a robust budgeting strategy. The key here is to be as proactive as possible.
Budgeting for compliance should not be an afterthought; it must be an integral part of an organization’s financial planning. This might involve setting aside a fixed percentage of revenue for compliance costs or having a separate compliance fund within the organization’s budget.
To make this process more effective, organizations can also consider historical data. Are certain regulations costing the organization more year after year? Looking back at the compliance costs over the past few years can help identify trends and patterns and forecast future expenses.
Allocating Resources for Ongoing Regulatory Changes
One of the immutable truths about regulatory compliance is that it's always in flux. New regulations can emerge, and existing ones can be revised, which necessitates an agile approach to resource allocation. Here, flexibility is your ally. Allocate resources in a way that can be adjusted as new regulations come into play.
Moreover, adopting a strategic approach to training can significantly reduce costs. Instead of generic, broad-spectrum training, focus on targeted training that addresses the specific regulations that impact your business the most. This ensures your employees are well-equipped to deal with relevant compliance issues without allocating resources toward unnecessary or irrelevant training.
Deploying Regulatory Compliance Solutions
Leveraging regulatory compliance solutions can streamline compliance processes and reduce associated costs. These solutions automate data collection, analysis, and reporting tasks to enhance compliance monitoring, reporting, and risk management while saving time and resources for compliance teams. Capabilities for automated regulatory horizon scanning help organizations stay on top of regulatory changes and proactively adjust their compliance strategies. For example, software that automatically captures relevant regulatory updates ensures that organizations are always working with the most current compliance requirements, eliminating the need for constant manual monitoring.
While technology-driven solutions are crucial, effectively managing compliance costs also hinges on strategic planning, process improvement, and cultural shifts. Organizations deploying these strategies can achieve substantial cost savings without compromising compliance quality or business agility.
Centralize Compliance Management
Implementing a centralized compliance management system consolidates all compliance-related tasks, data, and documentation into a single platform accessible across departments. This reduces costly redundancies, eliminates inefficiencies from duplicated efforts, and fosters consistent policy enforcement. Centralization enhances visibility into compliance risk areas and facilitates faster decision-making. For example, instead of multiple teams maintaining separate regulatory assessments or audit records, a unified system standardizes processes and streamlines workflows. This consolidation also simplifies managing compliance evidence during audits and inspections, significantly lowering administrative overhead and document retrieval time.
Risk-Based Prioritization
Not all compliance obligations present equal risk or potential penalties. By adopting a risk-based approach, organizations prioritize compliance efforts toward regulations with the greatest impact on business objectives and regulatory exposure. This targeted allocation of resources avoids overextending teams on low-risk requirements, improving overall efficiency.
To implement this, firms conduct thorough risk assessments to categorize compliance tasks based on potential financial, operational, or reputational consequences. Resources, training, and monitoring are then concentrated on critical controls, enabling organizations to address high-stakes areas proactively and cost-effectively.
Regular Compliance Audits with Technology
Although audits are sometimes viewed as a cost center, regular internal audits can generate long-term savings by uncovering gaps and inefficiencies early. Using compliance software automates audit scheduling, data collection, testing, and reporting, reducing manual labor and human error.
Automated audits provide continuous monitoring, real-time alerts for issues, and easy access to audit trails—all of which mitigate the risk of non-compliance penalties. By identifying systemic weaknesses proactively, organizations can implement corrective actions efficiently, preventing costly violations and reputational damage.
Review and Revise Policies
Compliance teams should regularly review organizational policies, standards, and procedures to ensure they remain relevant and efficient. Outdated or redundant policies often create unnecessary compliance burdens and slow down processes.
Streamlining document review workflows and approval chains eliminates bottlenecks, reduces cycle times, and frees personnel from jumping through undue procedural hoops. This simplification drives productivity, enabling the team to focus on value-added compliance activities rather than excessive administrative tasks.
Foster a Genuine Culture of Collaboration
Silos and poor communication create overlaps, gaps, and slow responses that increase compliance costs. Establishing cross-functional teams promotes knowledge sharing and innovative problem-solving, ensuring compliance is integrated into everyday business operations rather than treated as an isolated function.
Organizations benefit from implementing collaboration platforms and encouraging regular cross-departmental interaction, making expertise easily accessible. Smooth, seamless processes enable teams to concentrate on critical compliance risks and strategic initiatives rather than wasting time on redundant or manual tasks.
Additional Best Practices
- Automate Routine Tasks: Using AI and robotic process automation for routine compliance work like data collection, reporting, and monitoring cuts manual input and error risk.
- Training Tailored to Risk Areas: Targeted, role-specific training maximizes impact, reducing unnecessary resource expenditure on broad, irrelevant courses.
- Leverage Predictive Analytics: Analytics tools forecast compliance risk trends and prioritize audits and controls, improving effectiveness and cutting waste.
- Outsource Non-Core Activities: Strategic outsourcing of certain compliance functions (e.g., specialized audit services) can reduce fixed costs and improve scalability.
Costs represent averages and may vary widely depending on company size and geographic scope.
The MetricStream Compliance Management software helps organizations streamline firm-wide compliance programs with automated workflows and an integrated approach, driving significant time and cost savings. The centralized repository helps align regulations, standards, policies, and controls to provide 360-degree visibility into the compliance posture and eliminate inefficiencies and redundancies. Organizations are able to proactively identify control gaps and weaknesses while powerful dashboards and reports provide real-time insights into compliance processes.
To learn more about MetricStream Compliance Management, request a personalized demo today.
What is the average cost of compliance in 2025?
The average U.S. organization spends about $10,000 per employee annually on compliance, with large firms incurring costs in the millions or hundreds of millions, depending on sector and scale.
What industries face the highest compliance costs?
Financial services, healthcare, and technology sectors bear the highest compliance expenses due to stringent regulations and complexity, with finance and healthcare spending up to hundreds of millions annually.
How can automation reduce compliance expenses?
Automation minimizes manual effort, streamlines compliance workflows, reduces risk of human error, and lowers ongoing monitoring and reporting costs, ultimately driving significant savings and operational efficiency.
How do AI regulations affect compliance costs?
AI regulations, such as the EU AI Act, introduce new mandatory requirements including documentation, risk assessments, audits, and certifications. These add substantial annual compliance costs estimated around €52,000 per model and require specialized governance resources.








