Introduction
Gone are the days when digitization was merely a buzzword meant to signify technological trends. Today, enterprises hinge on intricate networks and sophisticated software solutions that puppeteer organizational workflows. And in times like this, the integrity of IT infrastructure has never been more critical.
The company's website crashes, confidential data is compromised, and operations grind to a halt. A nightmare scenario for many organizations.
And also a costly reality that underscores the dire need for effective IT risk management (ITRM). This article outlines what is IT Risk Management (ITRM), covering key steps in the ITRM process, including essential ITRM frameworks, best practices, policies, and tools to manage IT risks.
Key Takeaways:
- IT risk management (ITRM) is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with information technology systems and operations. It involves evaluating potential threats to IT assets, such as data breaches, cyber-attacks, system failures, and compliance violations, and implementing controls to minimize these risks.
- An effective IT risk management program safeguards companies against data breaches, system outages, and compliance violations, ensuring the integrity and availability of critical IT assets.
- IT risks include security threats like cyberattacks, data privacy concerns, hardware and software vulnerabilities, human errors, and natural disasters that can compromise an organization’s IT infrastructure and assets. Each poses unique challenges requiring proactive risk management strategies.
- The IT risk management process involves establishing context, identifying and assessing risks, implementing controls, and continuously monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of risk management efforts
- ISO 27001, COBIT, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework are some of the widely used frameworks that provide structured guidance for implementing robust IT risk management strategies.
What is IT Risk Management?
IT risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks associated with an organization’s information technology systems and processes. ITRM acts as a safeguard, designed to protect an organization's data integrity, availability, and confidentiality.
The potential consequences of unmanaged IT risks include but are not limited to, data breaches, system outages, and compliance violations, all of which can severely impact an organization's operations and reputation.
While it shares a common goal with general risk management, that is, minimizing risks to acceptable levels, ITRM is specifically tailored to address the unique challenges and threats in the digital and technological landscape.
The difference between the two lies in the specificity of IT risk management’s focus on IT systems and data, whereas general risk management encompasses a broader scope, including financial, legal, and operational risks.
Types of IT Risks
Let's delve into some of the types of IT risks, shedding light on their nuances and implications:
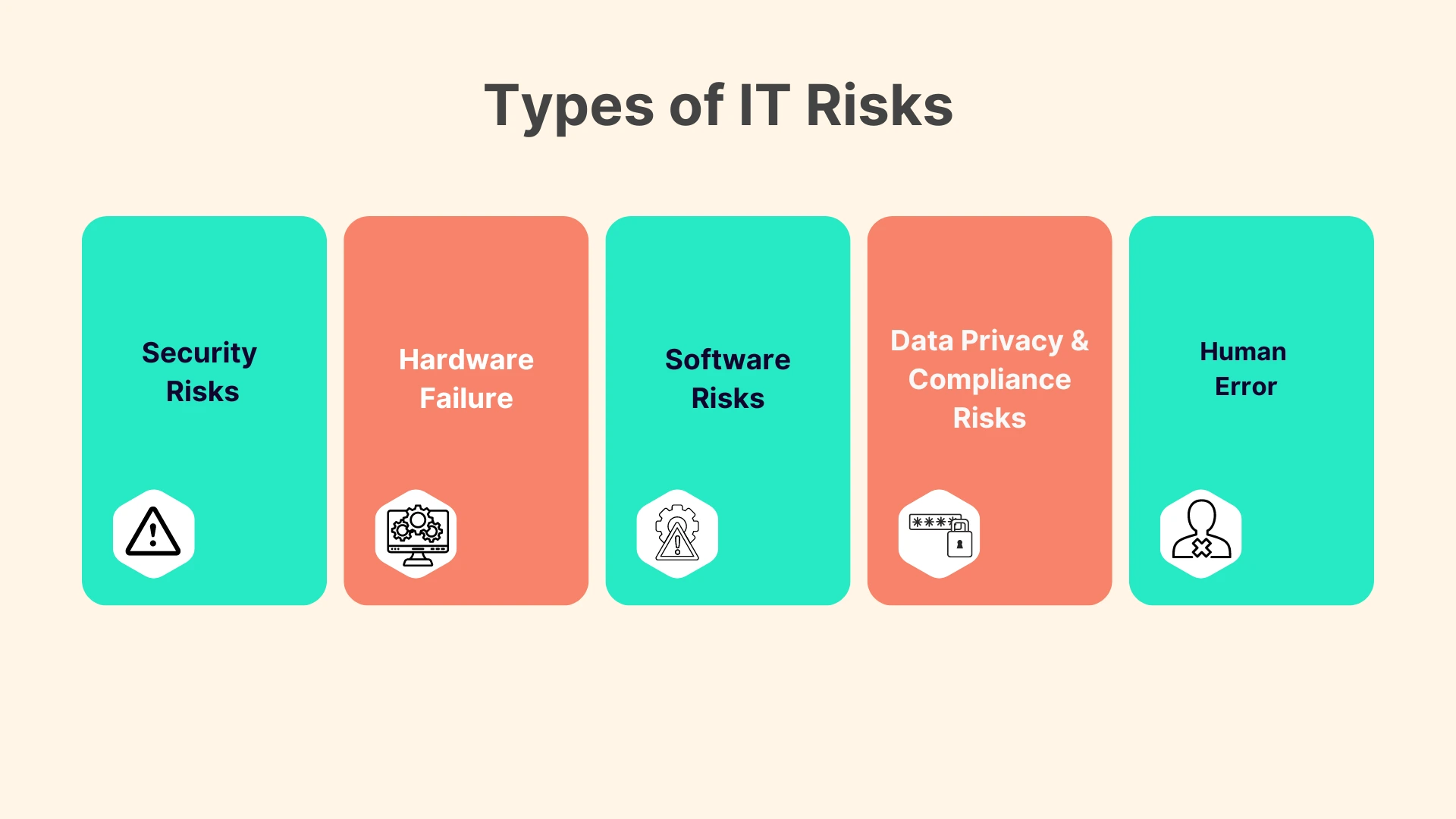
Security Risks
These include cyberattacks such as phishing, ransomware, and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks, aiming to breach data integrity and confidentiality. For instance, a successful phishing attack could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information, potentially resulting in financial loss and damage to customer trust.
Hardware Failure
The physical backbone of IT infrastructure, including servers, computers, and networking equipment, is prone to failure. Whether due to wear and tear, manufacturing defects, or external factors like power surges, natural disasters, etc. hardware failure can lead to significant downtime and data loss. A case in point would be a server crash in a data center, disrupting services for countless users and enterprises reliant on cloud storage and computing.
Software Risks
Software systems are not immune to risks, with vulnerabilities ranging from coding errors to outdated software. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or disrupt services. An example is the infamous Heartbleed bug, which exposed millions of users' sensitive data across the web due to a flaw in the OpenSSL cryptographic software library.
Data Privacy and Compliance Risks
With regulations like the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California, data privacy has become a critical concern for businesses worldwide. Failure to comply can not only result in hefty fines and legal consequences but also put sensitive information at risk. For instance, the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica data scandal highlighted the ramifications of neglecting data privacy and compliance risks, affecting millions of users’ personal information.
Human Error
Human error is a pervasive risk in IT, often overlooked. This includes misconfigurations, accidental data deletion, falling for phishing scams, etc. A simple mistake, like an employee mistakenly sending sensitive information to the wrong recipient, can have far-reaching consequences for data privacy and security.
What are the Steps in the IT Risk Management Process?
Here are the key steps that organizations need to follow to manage IT risks effectively:
Establish the Context
Understanding the organizational objectives, the IT environment, and the legal and regulatory landscape sets the stage for effective IT risk management. This foundational step ensures that all subsequent activities are aligned with the organization's overarching goals and compliance requirements.
Identify Risks
This involves cataloging potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities in the IT system. It covers any event that could negatively impact IT assets, from cyber attacks (e.g., malware, phishing) to natural disasters.
Assess Risks
Not all risks are created equal. In this step, risk teams evaluate the likelihood of each risk occurring and its potential impact on the organization. This risk assessment helps in prioritizing the risks based on their severity.
Implement Controls
Based on the risk assessment, an organization implements controls to mitigate the identified risks. These can be technical solutions like firewalls and encryption, policy changes, or training programs to educate employees about cybersecurity best practices.
Monitor and Review
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of implemented controls and review them regularly to ensure they are aligned with the changing IT environment and business objectives. This is not a 'set it and forget it' process - it’s an ongoing journey of vigilance and adaptation.
Communicate and Consult
Engage with stakeholders across the organization, from IT staff to senior management, ensuring everyone understands their role in safeguarding the organization’s digital assets. Open lines of communication foster a culture of security awareness and collaboration.
IT Risk Management Frameworks
These frameworks offer organizations valuable guidance and best practices for implementing effective IT risk management strategies. Some of the IT Risk Management frameworks can be tailored to meet specific organizational needs, industry requirements, and regulatory obligations, providing a flexible and scalable approach to managing IT risks.
Here are some valuable frameworks companies can abide by:
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It outlines requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an organization's information security management system (ISMS). The standard emphasizes a risk-based approach to information security, enabling organizations to identify, assess, and treat information security risks effectively.
ISO 27001 helps businesses protect confidential data, comply with legal and regulatory requirements, and enhance overall cybersecurity resilience.
By achieving ISO 27001 certification, organizations demonstrate their commitment to information security and gain credibility with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies)
COBIT is a comprehensive framework developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) that provides guidance for IT governance and management. It focuses on defining control objectives across various IT processes, covering areas such as risk management, information security, compliance, and strategic alignment.
By adopting COBIT, organizations can enhance transparency, accountability, and governance over IT processes, leading to improved business performance and risk management practices.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is a voluntary framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to improve cybersecurity risk management for organizations of all sizes and sectors.
This framework provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks by organizing existing standards, guidelines, and practices into five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. The NIST CSF 2.0 has added one more core function - Govern - for ensuring that “an organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy, expectations, and policy are established, communicated, and monitored.”
Organizations can use the CSF to assess and strengthen their cybersecurity posture, prioritize investments in cybersecurity resources, and communicate cybersecurity requirements internally and externally.
NIST SP800-53
This NIST framework provides a list of standards and guidelines for information systems in operations, management, and technical domains. These guidelines are multi-tiered, classified into low, moderate, and high controls based on the risk impact. It also introduces baselines that can act as starting points for organizations to secure their information systems and infrastructure.
SOC 2
SOC 2 is applicable to all technology service providers and highlights the criteria for information security specifically focusing on the safety and privacy of customer data. This framework is based on five trust principles which include security and availability along with processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Implementing an IT Risk Management Program
Implementing an effective IT risk management (ITRM) program is crucial for safeguarding digital assets and involves a number of steps. This includes developing a clear risk management policy outlining objectives, scope, and guidelines; assigning roles and responsibilities to streamline accountability; deploying the right risk management tools, like assessment tools and monitoring dashboards, to stay ahead of threats; training employees to raise awareness about IT risks and foster a risk-aware culture, and more.
Here's a practical guide to setting up an effective ITRM program within an organization:
Develop a Risk Management Policy
IT and risk teams can start by crafting a risk management policy that acts as the foundation of the program. This policy should not only outline the objectives and scope of ITRM efforts but also set clear guidelines for risk identification, assessment, mitigation, and monitoring. Organizations can leverage industry frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and others to ensure their approach is aligned to industry best practices.
Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Risk management is a team sport. It's critical to define clear roles and responsibilities for individuals or groups within an organization. This delegation encompasses tasks ranging from risk assessment to implementing mitigation strategies. Clearly defined roles ensure accountability and streamline the risk management process, making it more effective and less prone to oversight.
Select Risk Management Tools
The right tools can significantly amplify risk management efforts. Today’s market offers a plethora of software solutions designed to automate and enhance the risk management process. From risk assessment tools to monitoring dashboards, selecting the right mix can help organizations stay ahead of potential IT threats efficiently.
Train Employees and Raise Awareness
Ultimately, the success of any risk management program depends on the people behind it. Training employees and raising awareness about IT risks and their potential impacts on the organization are indispensable steps. Regular training sessions, workshops, and informative communications can foster a risk-aware culture within the organization.
Importance of IT Risk Management
IT risk management is important for businesses for a number of reasons, including:
Better Visibility into IT Risks
A comprehensive and robust IT risk management program improves an organization’s visibility into IT risks and control environment. It enables businesses to proactively mitigate risks and control gaps and weaknesses to ensure the resilience of the IT infrastructure.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
A diligent approach to risk management fortifies defenses by minimizing vulnerabilities and safeguarding sensitive information. This is paramount in instilling confidence among stakeholders and customers, assuring them that their data is in safe hands.
Improved Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
ITRM is synonymous with readiness. By identifying potential IT threats and preparing accordingly, organizations can ensure minimal interruption to their operations. This preparedness is crucial for maintaining service availability and functionality, even in the face of disruptions.
Increased Compliance with Regulations
ITRM ensures that organizations are not just reactive but proactive in meeting regulatory requirements, thus avoiding hefty fines and legal complications.
Cost Savings from Preventing Security Incidents
While investing in ITRM might seem like a substantial upfront cost, it is economically prudent in the long run. Preventing data breaches and IT failures through a well-crafted risk management strategy averts potential losses from recovery efforts, legal fees, and reputational damage.
IT Risk Management Best Practices
As businesses increasingly rely on technology, IT risk management has become essential for safeguarding systems, data, and operations. Effective IT risk management minimizes cybersecurity threats, ensures compliance, and enhances business continuity. Below are the best practices organizations should follow to manage IT risks effectively.
1. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Performing routine risk assessments helps organizations identify vulnerabilities, threats, and potential impacts. Use frameworks like NIST, ISO 27001, or FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) to evaluate risks based on their likelihood and severity.
2. Implement Strong Access Controls
Restricting unauthorized access to critical systems and data is crucial. Best practices include:
- Enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Using role-based access control (RBAC)
- Regularly reviewing and revoking outdated permissions
3. Keep Systems and Software Updated
Outdated software can introduce security vulnerabilities. Organizations should:
- Apply patches and updates regularly
- Automate updates for operating systems, applications, and security tools
- Monitor for emerging threats that may require urgent fixes
4. Strengthen Data Protection and Encryption
Data breaches can be costly and damaging. Protect sensitive data by:
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit
- Implementing backup and disaster recovery solutions
- Enforcing data loss prevention (DLP) measures
5. Develop a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan
Having a structured response plan helps organizations react swiftly to cyber incidents. An effective plan should include:
- Defined roles and responsibilities
- Incident detection, containment, and remediation protocols
- A post-incident review process to improve future response efforts
6. Train Employees on IT Security Awareness
Human error remains a major cybersecurity risk. Conduct regular training and simulations to educate employees about:
- Phishing attacks and social engineering threats
- Safe password practices and credential management
- Secure data handling and device usage
7. Monitor and Log IT Activities
Continuous network monitoring and logging help detect suspicious activities and prevent attacks. Organizations should:
- Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools
- Enable real-time alerts for anomalies
- Regularly review audit logs for unauthorized access attempts
8. Ensure Compliance with Industry Standards
Different industries have specific compliance regulations, such as:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for data privacy
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare security
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for financial transactions
Following these standards ensures regulatory adherence and reduces legal risks.
9. Establish Vendor and Third-Party Risk Management
Third-party vendors can introduce security vulnerabilities. Best practices include:
- Conducting due diligence and risk assessments for all vendors
- Establishing security and compliance requirements in contracts
- Regularly monitoring vendor cybersecurity practices
10. Continuously Improve IT Risk Management Strategies
IT risks evolve constantly, so organizations must regularly update their risk management strategies. This involves:
- Staying informed about emerging cybersecurity threats
- Updating policies and procedures based on new risks
- Conducting annual security audits and penetration testing
Implementing best practices in IT risk management helps businesses reduce vulnerabilities, protect critical assets, and ensure operational continuity. By adopting a proactive and adaptive approach, organizations can stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain a robust security posture in today’s digital landscape.
Why Choose MetricStream?
When it comes to translating the theoretical framework of an ITRM program into practical, actionable outcomes, MetricStream can be your ideal choice. MetricStream offers comprehensive tools and capabilities tailored for IT risk management, empowering organizations to mitigate IT risks effectively and adapt to cybersecurity challenges. Organizations can adapt swiftly to evolving cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and security of critical IT assets while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
The depth and breadth of its capabilities cater specifically to the nuanced needs of IT risk management.
Whether it’s through quantifying cyber risks in monetary terms or offering a centralized view of the organization's risk posture, MetricStream equips you with the tools and insights necessary to mitigate all levels of IT risks.
Moreover, its scalable architecture grows with your business, ensuring that your ITRM program remains robust and responsive to changing risk landscapes.
To learn more about MetricStream IT and Cyber Risk Management, request a personalized demo today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is IT risk?
MđT risk refers to any threat that may arise from a breach of security, non-compliance, lack of availability, or poor performance of IT resources that can affect the data, processes, and systems of an organization. IT risk also includes the risk that may arise from the IT systems of an organization.
What are common IT risk mitigation strategies?
Common IT risk mitigation strategies include implementing robust cybersecurity controls, conducting regular backups of critical data, providing employee training on security best practices, monitoring network activities for anomalies, and establishing incident response plans.
What are examples of IT risks that organizations face?
Examples of IT risks include data breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing scams, software vulnerabilities, system outages, insider threats, non-compliance with regulatory standards, third-party security issues, and natural disasters and catastrophes.
What role does regulatory compliance play in IT risk management?
Regulatory compliance ensures that organizations adhere to legal requirements related to IT security, data privacy, and risk management. Compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others define specific controls and practices that organizations must implement to mitigate IT risks and protect sensitive information.
What is meant by IT risk management?
IT risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks related to information technology, such as cybersecurity threats, system failures, and data breaches, to ensure business continuity and security.
What are the three major types of IT risks?
The three major types of IT risks are cybersecurity risks (e.g., hacking, malware attacks), operational risks (e.g., system failures, software bugs), and compliance risks (e.g., data privacy violations, regulatory non-compliance).
What are the stages of risk management?
The key stages of risk management include risk identification (detecting potential threats), risk assessment (analyzing likelihood and impact), risk mitigation (implementing controls), monitoring (ongoing evaluation), and response planning (reacting to incidents effectively).
Gone are the days when digitization was merely a buzzword meant to signify technological trends. Today, enterprises hinge on intricate networks and sophisticated software solutions that puppeteer organizational workflows. And in times like this, the integrity of IT infrastructure has never been more critical.
The company's website crashes, confidential data is compromised, and operations grind to a halt. A nightmare scenario for many organizations.
And also a costly reality that underscores the dire need for effective IT risk management (ITRM). This article outlines what is IT Risk Management (ITRM), covering key steps in the ITRM process, including essential ITRM frameworks, best practices, policies, and tools to manage IT risks.
- IT risk management (ITRM) is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with information technology systems and operations. It involves evaluating potential threats to IT assets, such as data breaches, cyber-attacks, system failures, and compliance violations, and implementing controls to minimize these risks.
- An effective IT risk management program safeguards companies against data breaches, system outages, and compliance violations, ensuring the integrity and availability of critical IT assets.
- IT risks include security threats like cyberattacks, data privacy concerns, hardware and software vulnerabilities, human errors, and natural disasters that can compromise an organization’s IT infrastructure and assets. Each poses unique challenges requiring proactive risk management strategies.
- The IT risk management process involves establishing context, identifying and assessing risks, implementing controls, and continuously monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of risk management efforts
- ISO 27001, COBIT, and the NIST Cybersecurity Framework are some of the widely used frameworks that provide structured guidance for implementing robust IT risk management strategies.
IT risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks associated with an organization’s information technology systems and processes. ITRM acts as a safeguard, designed to protect an organization's data integrity, availability, and confidentiality.
The potential consequences of unmanaged IT risks include but are not limited to, data breaches, system outages, and compliance violations, all of which can severely impact an organization's operations and reputation.
While it shares a common goal with general risk management, that is, minimizing risks to acceptable levels, ITRM is specifically tailored to address the unique challenges and threats in the digital and technological landscape.
The difference between the two lies in the specificity of IT risk management’s focus on IT systems and data, whereas general risk management encompasses a broader scope, including financial, legal, and operational risks.
Let's delve into some of the types of IT risks, shedding light on their nuances and implications:

Security Risks
These include cyberattacks such as phishing, ransomware, and DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks, aiming to breach data integrity and confidentiality. For instance, a successful phishing attack could lead to unauthorized access to sensitive information, potentially resulting in financial loss and damage to customer trust.
Hardware Failure
The physical backbone of IT infrastructure, including servers, computers, and networking equipment, is prone to failure. Whether due to wear and tear, manufacturing defects, or external factors like power surges, natural disasters, etc. hardware failure can lead to significant downtime and data loss. A case in point would be a server crash in a data center, disrupting services for countless users and enterprises reliant on cloud storage and computing.
Software Risks
Software systems are not immune to risks, with vulnerabilities ranging from coding errors to outdated software. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access or disrupt services. An example is the infamous Heartbleed bug, which exposed millions of users' sensitive data across the web due to a flaw in the OpenSSL cryptographic software library.
Data Privacy and Compliance Risks
With regulations like the GDPR in Europe and the CCPA in California, data privacy has become a critical concern for businesses worldwide. Failure to comply can not only result in hefty fines and legal consequences but also put sensitive information at risk. For instance, the Facebook-Cambridge Analytica data scandal highlighted the ramifications of neglecting data privacy and compliance risks, affecting millions of users’ personal information.
Human Error
Human error is a pervasive risk in IT, often overlooked. This includes misconfigurations, accidental data deletion, falling for phishing scams, etc. A simple mistake, like an employee mistakenly sending sensitive information to the wrong recipient, can have far-reaching consequences for data privacy and security.
Here are the key steps that organizations need to follow to manage IT risks effectively:
Establish the Context
Understanding the organizational objectives, the IT environment, and the legal and regulatory landscape sets the stage for effective IT risk management. This foundational step ensures that all subsequent activities are aligned with the organization's overarching goals and compliance requirements.
Identify Risks
This involves cataloging potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities in the IT system. It covers any event that could negatively impact IT assets, from cyber attacks (e.g., malware, phishing) to natural disasters.
Assess Risks
Not all risks are created equal. In this step, risk teams evaluate the likelihood of each risk occurring and its potential impact on the organization. This risk assessment helps in prioritizing the risks based on their severity.
Implement Controls
Based on the risk assessment, an organization implements controls to mitigate the identified risks. These can be technical solutions like firewalls and encryption, policy changes, or training programs to educate employees about cybersecurity best practices.
Monitor and Review
Continuously monitor the effectiveness of implemented controls and review them regularly to ensure they are aligned with the changing IT environment and business objectives. This is not a 'set it and forget it' process - it’s an ongoing journey of vigilance and adaptation.
Communicate and Consult
Engage with stakeholders across the organization, from IT staff to senior management, ensuring everyone understands their role in safeguarding the organization’s digital assets. Open lines of communication foster a culture of security awareness and collaboration.
These frameworks offer organizations valuable guidance and best practices for implementing effective IT risk management strategies. Some of the IT Risk Management frameworks can be tailored to meet specific organizational needs, industry requirements, and regulatory obligations, providing a flexible and scalable approach to managing IT risks.
Here are some valuable frameworks companies can abide by:
ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is an internationally recognized standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It outlines requirements for establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an organization's information security management system (ISMS). The standard emphasizes a risk-based approach to information security, enabling organizations to identify, assess, and treat information security risks effectively.
ISO 27001 helps businesses protect confidential data, comply with legal and regulatory requirements, and enhance overall cybersecurity resilience.
By achieving ISO 27001 certification, organizations demonstrate their commitment to information security and gain credibility with customers, partners, and stakeholders.
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies)
COBIT is a comprehensive framework developed by ISACA (Information Systems Audit and Control Association) that provides guidance for IT governance and management. It focuses on defining control objectives across various IT processes, covering areas such as risk management, information security, compliance, and strategic alignment.
By adopting COBIT, organizations can enhance transparency, accountability, and governance over IT processes, leading to improved business performance and risk management practices.
NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF)
The NIST Cybersecurity Framework (CSF) is a voluntary framework developed by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) to improve cybersecurity risk management for organizations of all sizes and sectors.
This framework provides a structured approach to managing cybersecurity risks by organizing existing standards, guidelines, and practices into five core functions: Identify, Protect, Detect, Respond, and Recover. The NIST CSF 2.0 has added one more core function - Govern - for ensuring that “an organization’s cybersecurity risk management strategy, expectations, and policy are established, communicated, and monitored.”
Organizations can use the CSF to assess and strengthen their cybersecurity posture, prioritize investments in cybersecurity resources, and communicate cybersecurity requirements internally and externally.
NIST SP800-53
This NIST framework provides a list of standards and guidelines for information systems in operations, management, and technical domains. These guidelines are multi-tiered, classified into low, moderate, and high controls based on the risk impact. It also introduces baselines that can act as starting points for organizations to secure their information systems and infrastructure.
SOC 2
SOC 2 is applicable to all technology service providers and highlights the criteria for information security specifically focusing on the safety and privacy of customer data. This framework is based on five trust principles which include security and availability along with processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
Implementing an effective IT risk management (ITRM) program is crucial for safeguarding digital assets and involves a number of steps. This includes developing a clear risk management policy outlining objectives, scope, and guidelines; assigning roles and responsibilities to streamline accountability; deploying the right risk management tools, like assessment tools and monitoring dashboards, to stay ahead of threats; training employees to raise awareness about IT risks and foster a risk-aware culture, and more.
Here's a practical guide to setting up an effective ITRM program within an organization:
Develop a Risk Management Policy
IT and risk teams can start by crafting a risk management policy that acts as the foundation of the program. This policy should not only outline the objectives and scope of ITRM efforts but also set clear guidelines for risk identification, assessment, mitigation, and monitoring. Organizations can leverage industry frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST CSF, and others to ensure their approach is aligned to industry best practices.
Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Risk management is a team sport. It's critical to define clear roles and responsibilities for individuals or groups within an organization. This delegation encompasses tasks ranging from risk assessment to implementing mitigation strategies. Clearly defined roles ensure accountability and streamline the risk management process, making it more effective and less prone to oversight.
Select Risk Management Tools
The right tools can significantly amplify risk management efforts. Today’s market offers a plethora of software solutions designed to automate and enhance the risk management process. From risk assessment tools to monitoring dashboards, selecting the right mix can help organizations stay ahead of potential IT threats efficiently.
Train Employees and Raise Awareness
Ultimately, the success of any risk management program depends on the people behind it. Training employees and raising awareness about IT risks and their potential impacts on the organization are indispensable steps. Regular training sessions, workshops, and informative communications can foster a risk-aware culture within the organization.
IT risk management is important for businesses for a number of reasons, including:
Better Visibility into IT Risks
A comprehensive and robust IT risk management program improves an organization’s visibility into IT risks and control environment. It enables businesses to proactively mitigate risks and control gaps and weaknesses to ensure the resilience of the IT infrastructure.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
A diligent approach to risk management fortifies defenses by minimizing vulnerabilities and safeguarding sensitive information. This is paramount in instilling confidence among stakeholders and customers, assuring them that their data is in safe hands.
Improved Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
ITRM is synonymous with readiness. By identifying potential IT threats and preparing accordingly, organizations can ensure minimal interruption to their operations. This preparedness is crucial for maintaining service availability and functionality, even in the face of disruptions.
Increased Compliance with Regulations
ITRM ensures that organizations are not just reactive but proactive in meeting regulatory requirements, thus avoiding hefty fines and legal complications.
Cost Savings from Preventing Security Incidents
While investing in ITRM might seem like a substantial upfront cost, it is economically prudent in the long run. Preventing data breaches and IT failures through a well-crafted risk management strategy averts potential losses from recovery efforts, legal fees, and reputational damage.
As businesses increasingly rely on technology, IT risk management has become essential for safeguarding systems, data, and operations. Effective IT risk management minimizes cybersecurity threats, ensures compliance, and enhances business continuity. Below are the best practices organizations should follow to manage IT risks effectively.
1. Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Performing routine risk assessments helps organizations identify vulnerabilities, threats, and potential impacts. Use frameworks like NIST, ISO 27001, or FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) to evaluate risks based on their likelihood and severity.
2. Implement Strong Access Controls
Restricting unauthorized access to critical systems and data is crucial. Best practices include:
- Enforcing multi-factor authentication (MFA)
- Using role-based access control (RBAC)
- Regularly reviewing and revoking outdated permissions
3. Keep Systems and Software Updated
Outdated software can introduce security vulnerabilities. Organizations should:
- Apply patches and updates regularly
- Automate updates for operating systems, applications, and security tools
- Monitor for emerging threats that may require urgent fixes
4. Strengthen Data Protection and Encryption
Data breaches can be costly and damaging. Protect sensitive data by:
- Encrypting data at rest and in transit
- Implementing backup and disaster recovery solutions
- Enforcing data loss prevention (DLP) measures
5. Develop a Cybersecurity Incident Response Plan
Having a structured response plan helps organizations react swiftly to cyber incidents. An effective plan should include:
- Defined roles and responsibilities
- Incident detection, containment, and remediation protocols
- A post-incident review process to improve future response efforts
6. Train Employees on IT Security Awareness
Human error remains a major cybersecurity risk. Conduct regular training and simulations to educate employees about:
- Phishing attacks and social engineering threats
- Safe password practices and credential management
- Secure data handling and device usage
7. Monitor and Log IT Activities
Continuous network monitoring and logging help detect suspicious activities and prevent attacks. Organizations should:
- Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools
- Enable real-time alerts for anomalies
- Regularly review audit logs for unauthorized access attempts
8. Ensure Compliance with Industry Standards
Different industries have specific compliance regulations, such as:
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for data privacy
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) for healthcare security
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) for financial transactions
Following these standards ensures regulatory adherence and reduces legal risks.
9. Establish Vendor and Third-Party Risk Management
Third-party vendors can introduce security vulnerabilities. Best practices include:
- Conducting due diligence and risk assessments for all vendors
- Establishing security and compliance requirements in contracts
- Regularly monitoring vendor cybersecurity practices
10. Continuously Improve IT Risk Management Strategies
IT risks evolve constantly, so organizations must regularly update their risk management strategies. This involves:
- Staying informed about emerging cybersecurity threats
- Updating policies and procedures based on new risks
- Conducting annual security audits and penetration testing
Implementing best practices in IT risk management helps businesses reduce vulnerabilities, protect critical assets, and ensure operational continuity. By adopting a proactive and adaptive approach, organizations can stay ahead of evolving threats and maintain a robust security posture in today’s digital landscape.
When it comes to translating the theoretical framework of an ITRM program into practical, actionable outcomes, MetricStream can be your ideal choice. MetricStream offers comprehensive tools and capabilities tailored for IT risk management, empowering organizations to mitigate IT risks effectively and adapt to cybersecurity challenges. Organizations can adapt swiftly to evolving cyber threats, ensuring the integrity and security of critical IT assets while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
The depth and breadth of its capabilities cater specifically to the nuanced needs of IT risk management.
Whether it’s through quantifying cyber risks in monetary terms or offering a centralized view of the organization's risk posture, MetricStream equips you with the tools and insights necessary to mitigate all levels of IT risks.
Moreover, its scalable architecture grows with your business, ensuring that your ITRM program remains robust and responsive to changing risk landscapes.
To learn more about MetricStream IT and Cyber Risk Management, request a personalized demo today.
What is IT risk?
MđT risk refers to any threat that may arise from a breach of security, non-compliance, lack of availability, or poor performance of IT resources that can affect the data, processes, and systems of an organization. IT risk also includes the risk that may arise from the IT systems of an organization.
What are common IT risk mitigation strategies?
Common IT risk mitigation strategies include implementing robust cybersecurity controls, conducting regular backups of critical data, providing employee training on security best practices, monitoring network activities for anomalies, and establishing incident response plans.
What are examples of IT risks that organizations face?
Examples of IT risks include data breaches, ransomware attacks, phishing scams, software vulnerabilities, system outages, insider threats, non-compliance with regulatory standards, third-party security issues, and natural disasters and catastrophes.
What role does regulatory compliance play in IT risk management?
Regulatory compliance ensures that organizations adhere to legal requirements related to IT security, data privacy, and risk management. Compliance frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI DSS, and others define specific controls and practices that organizations must implement to mitigate IT risks and protect sensitive information.
What is meant by IT risk management?
IT risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks related to information technology, such as cybersecurity threats, system failures, and data breaches, to ensure business continuity and security.
What are the three major types of IT risks?
The three major types of IT risks are cybersecurity risks (e.g., hacking, malware attacks), operational risks (e.g., system failures, software bugs), and compliance risks (e.g., data privacy violations, regulatory non-compliance).
What are the stages of risk management?
The key stages of risk management include risk identification (detecting potential threats), risk assessment (analyzing likelihood and impact), risk mitigation (implementing controls), monitoring (ongoing evaluation), and response planning (reacting to incidents effectively).








